Structured learning algorithm for detection of nonobstructive and obstructive coronary plaque lesions from computed tomography angiography
- PMID: 26158081
- PMCID: PMC4478984
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.2.1.014003
Structured learning algorithm for detection of nonobstructive and obstructive coronary plaque lesions from computed tomography angiography
Abstract
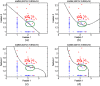
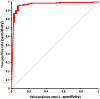
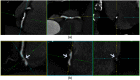
Visual identification of coronary arterial lesion from three-dimensional coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) remains challenging. We aimed to develop a robust automated algorithm for computer detection of coronary artery lesions by machine learning techniques. A structured learning technique is proposed to detect all coronary arterial lesions with stenosis [Formula: see text]. Our algorithm consists of two stages: (1) two independent base decisions indicating the existence of lesions in each arterial segment and (b) the final decision made by combining the base decisions. One of the base decisions is the support vector machine (SVM) based learning algorithm, which divides each artery into small volume patches and integrates several quantitative geometric and shape features for arterial lesions in each small volume patch by SVM algorithm. The other base decision is the formula-based analytic method. The final decision in the first stage applies SVM-based decision fusion to combine the two base decisions in the second stage. The proposed algorithm was applied to 42 CTA patient datasets, acquired with dual-source CT, where 21 datasets had 45 lesions with stenosis [Formula: see text]. Visual identification of lesions with stenosis [Formula: see text] by three expert readers, using consensus reading, was considered as a reference standard. Our method performed with high sensitivity (93%), specificity (95%), and accuracy (94%), with receiver operator characteristic area under the curve of 0.94. The proposed algorithm shows promising results in the automated detection of obstructive and nonobstructive lesions from CTA.
Keywords: coronary arterial disease; coronary arterial lesion detection from coronary computed tomography angiography; coronary computed tomography angiography; image feature extraction; learning-based detection; machine learning; structured learning; support vector machines; support vector regression.
Figures
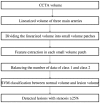

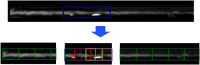

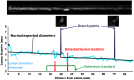

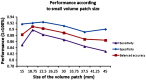
References
-
- Budoff M. J., et al. , “Diagnostic performance of 64-multidetector row coronary computed tomographic angiography for evaluation of coronary artery stenosis in individuals without known coronary artery disease: results from the prospective multicenter ACCURACY (Assessment by Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography of Individuals Undergoing Invasive Coronary Angiography) trial,” J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 52(21), 1724–1732 (2008).JACCDI10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hausleiter J., et al. , “Non-invasive coronary computed tomographic angiography for patients with suspected coronary artery disease: the Coronary Angiography by Computed Tomography with the Use of a Submillimeter resolution (CACTUS) trial,” Eur. Heart J. 28(24), 3034–3041 (2007).EHJODF10.1093/eurheartj/ehm150 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

