Association of three 8q24 polymorphisms with prostate cancer susceptibility: evidence from a meta-analysis with 50,854 subjects
- PMID: 26159557
- PMCID: PMC4498192
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12069
Association of three 8q24 polymorphisms with prostate cancer susceptibility: evidence from a meta-analysis with 50,854 subjects
Abstract
The 8q24 polymorphisms have been implicated in various cancers. Three 8q24 polymorphisms (rs1447295 C>A, rs16901979 C>A, and rs6983267 T>G) have been extensively investigated for their association with prostate cancer (PCa) susceptibility, yet conclusions are contradictory. We conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis to reevaluate the associations between those polymorphisms and PCa susceptibility, according to the latest meta-analysis guidelines (PRISMA). Eligible publications were searched from MEDLINE, EMBASE and CBM. False positive report possibility analysis was performed. We totally collected 20184 cases and 20439 controls from 20 studies for the rs1447295 C>A, 1850 cases and 2090 controls from 7 studies for the rs16901979 C>A, and 12233 cases and 7582 controls from 17 studies for the rs6983267 T>G. Overall, each of studied 8q24 polymorphisms was significantly associated with PCa risk individually. Significant associations were also observed in stratified analysis by ethnicity, source of control, and quality score. Interestingly, the effect of rs1447295 on PCa risk was observed among Caucasians and Asians, but not Africa-Americans. The effect of rs16901979 was more prominent among Africa-Americans than Asians. Likewise, rs6983267 conferred a higher Pca risk among Caucasians than Asians. Collectively, these 8q24 variant(s) may modulate PCa risk in an ethnic-specific manner.
Figures

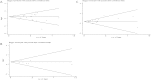

Similar articles
-
Association between genetic variations at 8q24 and prostate cancer risk in Mexican Men.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022 Sep;25(3):507-512. doi: 10.1038/s41391-021-00461-x. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022. PMID: 34599275
-
Association between 8q24 (rs13281615 and rs6983267) polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis involving 117,355 subjects.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 18;7(42):68002-68011. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12009. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27634905 Free PMC article.
-
Common 8q24 sequence variations are associated with Asian Indian advanced prostate cancer risk.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008 Sep;17(9):2431-5. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-2823. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008. PMID: 18768513 Free PMC article.
-
Racial disparities in the association between variants on 8q24 and prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncologist. 2012;17(3):312-20. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0315. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Oncologist. 2012. PMID: 22382457 Free PMC article.
-
8q24 rs4242382 polymorphism is a risk factor for prostate cancer among multi-ethnic populations: evidence from clinical detection in China and a meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(19):8311-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.19.8311. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25339022 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between genetic variations at 8q24 and prostate cancer risk in Mexican Men.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022 Sep;25(3):507-512. doi: 10.1038/s41391-021-00461-x. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022. PMID: 34599275
-
Association between 8q24 Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Cancer. 2017 Sep 15;8(16):3198-3211. doi: 10.7150/jca.20456. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29158792 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions Between Genome-Wide Significant Genetic Variants and Circulating Concentrations of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Relation to Prostate Cancer Risk in the National Cancer Institute BPC3.Am J Epidemiol. 2017 Mar 15;185(6):452-464. doi: 10.1093/aje/kww143. Am J Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28399564 Free PMC article.
-
Association between 8q24 rs6983267 polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis involving 170,737 subjects.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 4;8(34):57421-57439. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18960. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915683 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of WRAP53 in Cell Homeostasis and Carcinogenesis Onset.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Nov 4;44(11):5498-5515. doi: 10.3390/cimb44110372. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36354684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yeager M. et al. Genome-wide association study of prostate cancer identifies a second risk locus at 8q24. Nat Genet 39, 645–9 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

