Parkin regulates mitophagy and mitochondrial function to protect against alcohol-induced liver injury and steatosis in mice
- PMID: 26159696
- PMCID: PMC4556950
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00108.2015
Parkin regulates mitophagy and mitochondrial function to protect against alcohol-induced liver injury and steatosis in mice
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Jan 15;310(2):G142. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.zh3-7034-corr.2016. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26772614 Free PMC article.
Abstract
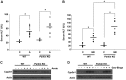
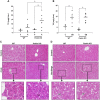
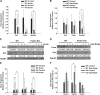
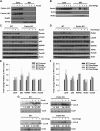
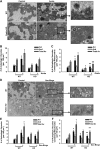
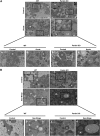
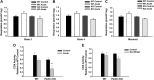
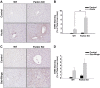
Alcoholic liver disease claims two million lives per year. We previously reported that autophagy protected against alcohol-induced liver injury and steatosis by removing damaged mitochondria. However, the mechanisms for removal of these mitochondria are unknown. Parkin is an evolutionarily conserved E3 ligase that is recruited to damaged mitochondria to initiate ubiquitination of mitochondrial outer membrane proteins and subsequent mitochondrial degradation by mitophagy. In addition to its role in mitophagy, Parkin has been shown to have other roles in maintaining mitochondrial function. We investigated whether Parkin protected against alcohol-induced liver injury and steatosis using wild-type (WT) and Parkin knockout (KO) mice treated with alcohol by the acute-binge and Gao-binge (chronic plus acute-binge) models. We found that Parkin protected against liver injury in both alcohol models, likely because of Parkin's role in maintaining a population of healthy mitochondria. Alcohol caused greater mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress in Parkin KO livers compared with WT livers. After alcohol treatment, Parkin KO mice had severely swollen and damaged mitochondria that lacked cristae, which were not seen in WT mice. Furthermore, Parkin KO mice had decreased mitophagy, β-oxidation, mitochondrial respiration, and cytochrome c oxidase activity after acute alcohol treatment compared with WT mice. Interestingly, liver mitochondria seemed able to adapt to alcohol treatment, but Parkin KO mouse liver mitochondria had less capacity to adapt to Gao-binge treatment compared with WT mouse liver mitochondria. Overall, our findings indicate that Parkin is an important mediator of protection against alcohol-induced mitochondrial damage, steatosis, and liver injury.
Keywords: Parkin; alcohol; autophagy; liver injury; mitophagy; steatosis.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


Comment in
-
Mitophagy in steatotic hepatocytes of ethanol-treated wild-type and Parkin knockout mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):G513-4. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00254.2015. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26374875 No abstract available.
-
Mitophagy, mitochondrial spheroids, and mitochondrial-derived vesicles in alcohol-induced liver injury.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):G515. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00264.2015. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26374876 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

