Decrease of miR-146a is associated with the aggressiveness of human oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 26159827
- PMCID: PMC4536106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.06.007
Decrease of miR-146a is associated with the aggressiveness of human oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
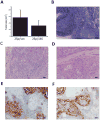
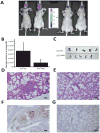
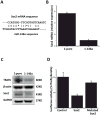
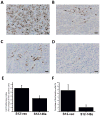
With the aim to identify microRNAs that may contribute to oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) progression, we compared the microRNA expression profiles of two related cell lines that form tumors with differential aggressiveness. A panel of 28 microRNAs was found to be more than 1.5-fold altered, among which miR-146a was the most significantly changed (-4.6-fold). Loss of miR-146a expression was validated in human high-grade tumors, while normal oral mucosa retained expression, using fluorescence in situ hybridization on a tissue microarray. Restoration of miR-146a in SCC25 and UMSCC1 cells decreased in vitro invasive activity, suppressed tumor growth in vivo, and decreased the incidence of UMSCC1 lung metastasis. The transcription factor Sox2 was found to be a putative target of miR-146a. In conclusion, the loss or decrease of miR-146a is a new feature that is associated with more aggressive behaviour in oral squamous carcinoma.
Keywords: Metastasis; MicroRNA; Oral cancer; miR-146a.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Assaying microRNA loss-of-function phenotypes in mammalian cells: emerging tools and their potential therapeutic utility. RNA Biol. 2009;6(5):541–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

