Structural Basis for Antigen Recognition by Transglutaminase 2-specific Autoantibodies in Celiac Disease
- PMID: 26160175
- PMCID: PMC4571865
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.669895
Structural Basis for Antigen Recognition by Transglutaminase 2-specific Autoantibodies in Celiac Disease
Abstract
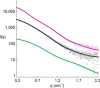
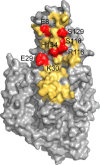
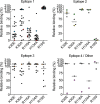
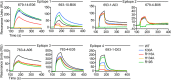
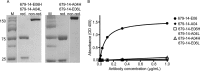
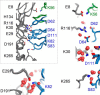
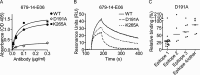
Antibodies to the autoantigen transglutaminase 2 (TG2) are a hallmark of celiac disease. We have studied the interaction between TG2 and an anti-TG2 antibody (679-14-E06) derived from a single gut IgA plasma cell of a celiac disease patient. The antibody recognizes one of four identified epitopes targeted by antibodies of plasma cells of the disease lesion. The binding interface was identified by small angle x-ray scattering, ab initio and rigid body modeling using the known crystal structure of TG2 and the crystal structure of the antibody Fab fragment, which was solved at 2.4 Å resolution. The result was confirmed by testing binding of the antibody to TG2 mutants by ELISA and surface plasmon resonance. TG2 residues Arg-116 and His-134 were identified to be critical for binding of 679-14-E06 as well as other epitope 1 antibodies. In contrast, antibodies directed toward the two other main epitopes (epitopes 2 and 3) were not affected by these mutations. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest interactions of 679-14-E06 with the N-terminal domain of TG2 via the CDR2 and CDR3 loops of the heavy chain and the CDR2 loop of the light chain. In addition there were contacts of the framework 3 region of the heavy chain with the catalytic domain of TG2. The results provide an explanation for the biased usage of certain heavy and light chain gene segments by epitope 1-specific antibodies in celiac disease.
Keywords: antibody; celiac disease; epitope mapping; mutagenesis; small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS); surface plasmon resonance (SPR); transglutaminase.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Abadie V., Sollid L. M., Barreiro L. B., Jabri B. (2011) Integration of genetic and immunological insights into a model of celiac disease pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 29, 493–525 - PubMed
-
- Dieterich W., Ehnis T., Bauer M., Donner P., Volta U., Riecken E. O., Schuppan D. (1997) Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat. Med. 3, 797–801 - PubMed
-
- Di Niro R., Mesin L., Zheng N. Y., Stamnaes J., Morrissey M., Lee J. H., Huang M., Iversen R., du Pré M. F., Qiao S. W., Lundin K. E., Wilson P. C., Sollid L. M. (2012) High abundance of plasma cells secreting transglutaminase 2-specific IgA autoantibodies with limited somatic hypermutation in celiac disease intestinal lesions. Nat. Med. 18, 441–445 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Husby S., Koletzko S., Korponay-Szabó I. R., Mearin M. L., Phillips A., Shamir R., Troncone R., Giersiepen K., Branski D., Catassi C., Lelgeman M., Mäki M., Ribes-Koninckx C., Ventura A., Zimmer K. P., ESPGHAN Working Group on Coeliac Disease Diagnosis, ESPGHAN Gastroenterology Committee, and European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (2012) European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition guidelines for the diagnosis of coeliac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 54, 136–160 - PubMed
-
- Dieterich W., Laag E., Schöpper H., Volta U., Ferguson A., Gillett H., Riecken E. O., Schuppan D. (1998) Autoantibodies to tissue transglutaminase as predictors of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 115, 1317–1321 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

