The Effect of Waterpipe Tobacco Smoke Exposure on Learning and Memory Functions in the Rat Model
- PMID: 26160697
- PMCID: PMC4575272
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-015-0613-7
The Effect of Waterpipe Tobacco Smoke Exposure on Learning and Memory Functions in the Rat Model
Abstract
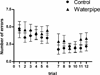
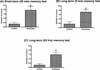
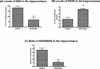
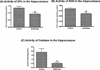
Tobacco smoking is a global health hazard that kills about 5 million people annually. Waterpipe smoking is among the most popular methods of tobacco consumption worldwide. In this study, we investigated whether waterpipe smoking impairs learning and memory in the hippocampus, a question of special concern due to the particular popularity of waterpipe use among youth. Additionally, possible molecular targets for expected learning and memory impairment were determined. In this study, rats were exposed to waterpipe smoke (WTS) by whole body exposure 1 h × 5 days/week, for 1 month, and outcomes were compared to a control group exposed only to fresh air. Outcomes included spatial learning and memory using the radial arm water maze (RAWM) and oxidative stress biomarkers (catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), oxidized glutathione (GSSG), GSH/GSSG ratio). We found that WTS exposure led to impaired short- and long-term memory. This impairment was accompanied by reduced hippocampal activity of catalase, SOD, GPx, GSH, and GSH/GSSG, elevated GSSG, thus marked changes in oxidative stress biomarkers. In conclusion, there is reason for concern that WTS exposure may impair cognitive ability.
Keywords: Hippocampus; Maze; Memory; Tobacco; Waterpipe.
Figures
References
-
- Aleisa AM, Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA. Nicotine prevents stress-induced enhancement of long-term depression in hippocampal area CA1: electrophysiological and molecular studies. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Aleisa AM, Helal G, Alhaider IA, Alzoubi KH, Srivareerat M, Tran TT, et al. Acute nicotine treatment prevents REM sleep deprivation-induced learning and memory impairment in rat. Hippocampus. 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

