Chlorogenic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury: the involvement of CYP450 metabolic enzymes and some antioxidant signals
- PMID: 26160718
- PMCID: PMC4506951
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1400346
Chlorogenic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury: the involvement of CYP450 metabolic enzymes and some antioxidant signals
Abstract
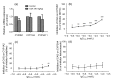
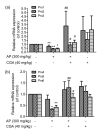
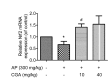
Chlorogenic acid (CGA), a polyphenolic compound, is abundant in fruits, dietary vegetables, and some medicinal herbs. This study investigated the prevention of CGA against acetaminophen (AP)-induced hepatotoxicity and its engaged mechanisms. CGA reversed the decreased cell viability induced by AP in L-02 cells in vitro. In addition, CGA reduced the AP-induced increased serum levels of alanine/aspartate aminotransferase (ALT/AST) in vivo. The effect of CGA on cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymatic (CYP2E1, CYP1A2, and CYP3A4) activities showed that CGA caused very little inhibition on CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 enzymatic activities, but not CYP3A4. The measurement of liver malondialdehyde (MDA), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and glutathione (GSH) levels showed that CGA prevented AP-induced liver oxidative stress injury. Further, CGA increased the AP-induced decreased mRNA expression of peroxiredoxin (Prx) 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, epoxide hydrolase (Ephx) 2, and polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide K (Polr2k), and nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). In summary, CGA ameliorates the AP-induced liver injury probably by slightly inhibiting CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 enzymatic properties. In addition, cellular important antioxidant signals such as Prx1, 2, 3, 5, 6, Ephx2, Polr2k, and Nrf2 also contributed to the protection of CGA against AP-induced oxidative stress injury.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; CYP450; Chlorogenic acid; Oxidative stress injury.
Conflict of interest statement
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Figures
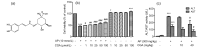


Similar articles
-
Chlorogenic acid, a dietary polyphenol, protects acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Nov;24(11):1911-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24011717
-
Natural Polyphenol Chlorogenic Acid Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Activating ERK/Nrf2 Antioxidative Pathway.Toxicol Sci. 2018 Mar 1;162(1):99-112. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx230. Toxicol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29136249
-
5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol (taxifolin) protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury by regulating the glutathione pathway.Life Sci. 2019 Nov 1;236:116939. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116939. Epub 2019 Oct 5. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31593705
-
Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential.Redox Biol. 2016 Dec;10:148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Redox Biol. 2016. PMID: 27744120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of cytochrome P450 in cisplatin treatment: implications for toxicity.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 Aug;80(2):223-233. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3358-x. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28612092 Review.
Cited by
-
The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: current state.Nutr J. 2016 Jul 25;15(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12937-016-0186-5. Nutr J. 2016. PMID: 27456681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of drug-induced liver injury and hepatoprotective effects of natural drugs.Chin Med. 2021 Dec 11;16(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00543-x. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34895294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chlorogenic Acid: A Systematic Review on the Biological Functions, Mechanistic Actions, and Therapeutic Potentials.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 23;16(7):924. doi: 10.3390/nu16070924. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38612964 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of aqueous leaf extracts of Chromolaena odorata and Tridax procumbens on doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats.Porto Biomed J. 2021 Dec 3;6(6):e143. doi: 10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000143. eCollection 2021 Nov-Dec. Porto Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34881354 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Phoenix dactylifera L. Seeds against Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats: A Comparison with Vitamin C.ScientificWorldJournal. 2021 Jul 6;2021:6618273. doi: 10.1155/2021/6618273. eCollection 2021. ScientificWorldJournal. 2021. PMID: 34326710 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

