Inhibition of miR-21 restores RANKL/OPG ratio in multiple myeloma-derived bone marrow stromal cells and impairs the resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts
- PMID: 26160841
- PMCID: PMC4694994
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4398
Inhibition of miR-21 restores RANKL/OPG ratio in multiple myeloma-derived bone marrow stromal cells and impairs the resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts
Abstract
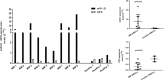
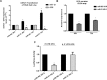
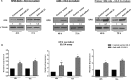
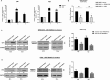
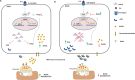
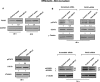
miR-21 is an oncogenic microRNA (miRNA) with an emerging role as therapeutic target in human malignancies, including multiple myeloma (MM). Here we investigated whether miR-21 is involved in MM-related bone disease (BD). We found that miR-21 expression is dramatically enhanced, while osteoprotegerin (OPG) is strongly reduced, in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) adherent to MM cells. On this basis, we validated the 3'UTR of OPG mRNA as miR-21 target. Constitutive miR-21 inhibition in lentiviral-transduced BMSCs adherent to MM cells restored OPG expression and secretion. Interestingly, miR-21 inhibition reduced RANKL production by BMSCs. Overexpression of protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3), which is a direct and validated target of miR-21, antagonized STAT3-mediated RANKL gene activation. Finally, we demonstrate that constitutive expression of miR-21 inhibitors in BMSCs restores RANKL/OPG balance and dramatically impairs the resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. Taken together, our data provide proof-of-concept that miR-21 overexpression within MM-microenviroment plays a crucial role in bone resorption/apposition balance, supporting the design of innovative miR-21 inhibition-based strategies for MM-related BD.
Keywords: OPG; RANKL; miR-21; miRNAs; multiple myeloma bone disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson KC, Alsina M, Bensinger W, Biermann JS, Chanan-Khan A, Cohen AD, Devine S, Djulbegovic B, Faber EA, Jr., Gasparetto C, Huff CA, Kassim A, Medeiros BC, Meredith R, Raje N, Schriber J, et al. Multiple myeloma. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 2011;9:1146–1183. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KC, Carrasco RD. Pathogenesis of myeloma. Annual review of pathology. 2011;6:249–274. - PubMed
-
- Giuliani N, Bataille R, Mancini C, Lazzaretti M, Barille S. Myeloma cells induce imbalance in the osteoprotegerin/osteoprotegerin ligand system in the human bone marrow environment. Blood. 2001;98:3527–3533. - PubMed
-
- Croucher PI, Shipman CM, Lippitt J, Perry M, Asosingh K, Hijzen A, Brabbs AC, van Beek EJ, Holen I, Skerry TM, Dunstan CR, Russell GR, Van Camp B, Vanderkerken K. Osteoprotegerin inhibits the development of osteolytic bone disease in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2001;98:3534–3540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

