Prophylactic Ozone Administration Reduces Intestinal Mucosa Injury Induced by Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion in the Rat
- PMID: 26161005
- PMCID: PMC4487723
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/792016
Prophylactic Ozone Administration Reduces Intestinal Mucosa Injury Induced by Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion in the Rat
Abstract
Objectives: Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury is associated with mucosal damage and has a high rate of mortality. Various beneficial effects of ozone have been shown. The aim of the present study was to show the effects of ozone in ischemia reperfusion model in intestine.
Material and method: Twenty eight Wistar rats were randomized into four groups with seven rats in each group. Control group was administered serum physiologic (SF) intraperitoneally (ip) for five days. Ozone group was administered 1 mg/kg ozone ip for five days. Ischemia Reperfusion (IR) group underwent superior mesenteric artery occlusion for one hour and then reperfusion for two hours. Ozone + IR group was administered 1 mg/kg ozone ip for five days and at sixth day IR model was applied. Rats were anesthetized with ketamine∖xyzlazine and their intracardiac blood was drawn completely and they were sacrificed. Intestinal tissue samples were examined under light microscope. Levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathioneperoxidase (GSH-Px), malondyaldehide (MDA), and protein carbonyl (PCO) were analyzed in tissue samples. Total oxidant status (TOS), and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) were analyzed in blood samples. Data were evaluated statistically by Kruskal Wallis test.
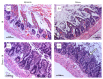
Results: In the ozone administered group, degree of intestinal injury was not different from the control group. IR caused an increase in intestinal injury score. The intestinal epithelium maintained its integrity and decrease in intestinal injury score was detected in Ozone + IR group. SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT values were high in ozone group and low in IR. TOS parameter was highest in the IR group and the TAC parameter was highest in the ozone group and lowest in the IR group.
Conclusion: In the present study, IR model caused an increase in intestinal injury.In the present study, ozone administration had an effect improving IR associated tissue injury. In the present study, ozone therapy prevented intestine from ischemia reperfusion injury. It is thought that the therapeutic effect of ozone is associated with increase in antioxidant enzymes and protection of cells from oxidation and inflammation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The protective effect of prophylactic ozone administration against retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017 Mar;36(1):39-47. doi: 10.3109/15569527.2016.1156120. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27028056
-
Ozone Prevents Cochlear Damage From Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Guinea Pigs.Artif Organs. 2017 Aug;41(8):744-752. doi: 10.1111/aor.12863. Epub 2017 Mar 5. Artif Organs. 2017. PMID: 28261890
-
Postconditioning Ozone Alleviates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Enhances Flap Endurance in Rats.J Invest Surg. 2020 Jan;33(1):15-24. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2018.1473901. Epub 2018 Oct 19. J Invest Surg. 2020. PMID: 30339503
-
Life and death at the mucosal-luminal interface: New perspectives on human intestinal ischemia-reperfusion.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar 7;22(9):2760-70. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2760. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26973414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the molecular complexity of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury through omics technologies.Proteomics. 2024 Jun;24(12-13):e2300160. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300160. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38477684 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in an Experimental Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Model in Rats: The Role of Ozone Therapy and Trimetazidine.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 25;14(9):1051. doi: 10.3390/biom14091051. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334818 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Oxygen-Ozone Therapy for Mesh Skin Graft in a Cat with a Hindlimb Extensive Wound.Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;13(3):513. doi: 10.3390/ani13030513. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766402 Free PMC article.
-
Is the increased ozone dosage key factor for its anti-inflammatory effect in an experimental model of mesenteric ischemia?Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023 Oct;29(10):1069-1074. doi: 10.14744/tjtes.2023.86086. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023. PMID: 37791435 Free PMC article.
-
Medical ozone therapy reduces oxidative stress and testicular damage in an experimental model of testicular torsion in rats.Int Braz J Urol. 2017 Nov-Dec;43(6):1160-1166. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0546. Int Braz J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28727368 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of local ozone treatment on rats with anterior rectal resection and the possible mechanisms.Biomed Eng Online. 2021 Aug 6;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12938-021-00918-z. Biomed Eng Online. 2021. PMID: 34362379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devesa E., Menéndez S., Rodriguez M. M., Gómez M., Garcia J. Ozone therapy in ischemic cerebro-vascular disease. Proceedings of the 11th Ozone World Congress; 1993; San Francisco, Calif, USA. pp. M-4-10–M-4-18.
-
- Werkmeister H. Dekubitalges chwüre und die Behandlung mit der Ozon-Unterdruckbegasung. In: Beck V.-H., editor. Ozon-Handbuck. Grundlagen. Prävention. Therapie. Landsberg am Lech, Germany: Ecomed; 1995. pp. V-7.11–V-7.12.
-
- Romero Valdés A., Menéndez Cepero S., Gómez Moraleda M., Ley Pozo J. Ozone therapy in the advanced stages of arteriosclerosis obliterans. Angiologia. 1993;45(4):146–148. - PubMed
-
- Menéndez S., Iglesias O., Bidot C., Puga R., Carballo A. International Ozone Association. Application of ozone therapy in children with humoral immunity deficiency. Proceedings of the 12th Ozone World Congress, Ozone in Medicine; 1995; Lille, France. pp. 271–274.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

