The relationship between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio and thrombolysis in myocardial infarction risk score in patients with ST elevation acute myocardial infarction before primary coronary intervention
- PMID: 26161105
- PMCID: PMC4495129
- DOI: 10.5114/pwki.2015.52286
The relationship between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio and thrombolysis in myocardial infarction risk score in patients with ST elevation acute myocardial infarction before primary coronary intervention
Abstract
Introduction: The thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) risk score is calculated as the sum of independent predictors of mortality and ischemic events in ST elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI). Several studies show that the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a prognostic inflammatory marker. In preliminary studies, platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) has been proposed as a pro-thrombotic marker. The relationship between NLR, PLR and TIMI risk score for STEMI has never been studied.
Aim: To evaluate the association between TIMI-STEMI risk score and NLR, PLR and other biochemical indices in STEMI.
Material and methods: In this retrospective study, we evaluated 390 patients who presented with STEMI within 12 h of symptom onset. Patients were grouped according to low and high TIMI risk scores.
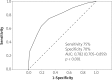
Results: We enrolled 390 patients (mean age 61.9 ±13.6 years; 73% were men). The NLR, platelet distribution width (PDW) and uric acid level (UA) were significantly associated with a high TIMI-STEMI risk score (p = 0.016, p = 0.008, p = 0.030, respectively), but PLR was not associated with a high TIMI-STEMI risk score. Left ventricular ejection fraction was an independent predictor of TIMI-STEMI risk score. A cut-off point of TIMI-STEMI score of > 4 predicted in-hospital mortality (sensitivity 75%, specificity 70%, p < 0.001). We found that NLR, PDW, and UA level were associated with TIMI-STEMI risk score.
Conclusions: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, PDW and UA level are convenient, inexpensive and reproducible biomarkers for STEMI prognosis before primary angioplasty when these indicators are combined with the TIMI-STEMI risk score. We believe that these significant findings can guide further clinical practice.
Keywords: STEMI; TIMI risk score; hematologic indices; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; platelet to lymphocyte ratio.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel predictors of infarct-related artery patency for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, uric acid, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.Anatol J Cardiol. 2015 Aug;15(8):648-56. doi: 10.5152/akd.2014.5592. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25550174 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with thrombolysis in myocardial infarction frame count in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Eur J Clin Invest. 2017 Apr;47(4):322-327. doi: 10.1111/eci.12736. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Eur J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28177528
-
Predictive value of admission red cell distribution width-platelet ratio for no-reflow phenomenon in acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Cardiol J. 2016;23(1):84-92. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0070. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Cardiol J. 2016. PMID: 26503078
-
Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 May 2;18(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0812-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29716535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hematological Indices in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:3041565. doi: 10.1155/2017/3041565. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 29109595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Marker of Inflammation: Azurocidin in Patients with ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 29;19(12):3797. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123797. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30501029 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with proximal/middle segment of the LAD lesions in patients with ST segment elevation infarction.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2016;41(4):386-391. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2016.65138. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28450802 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Systemic Inflammatory Immunologic Index and the Angiographic SYNTAX Score and the TIMI Flow Grade in Acute STEMI: A Cohort Study.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2021 Oct;16(4):147-155. doi: 10.18502/jthc.v16i4.8600. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2021. PMID: 35935551 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Poor Prognostic Predictors in Patients With an Initial Diagnosis of Autoimmune Encephalitis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 7;10:1286. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01286. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31231392 Free PMC article.
-
Independent Association of Thyroid Dysfunction and Inflammation Predicts Adverse Events in Patients with Heart Failure via Promoting Cell Death.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Aug 31;9(9):290. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9090290. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 36135435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, et al. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–57. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–74. - PubMed
-
- Pearson TA, Mensah GA, Alexander RW, et al. Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: application to clinical and public health practice. Circulation. 2003;107:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Zairis MN, Lyras AG, Bibis GP, et al. Association of inflammatory biomarkers and cardiac troponin I with multifocal activation of coronary artery tree in the setting of non-ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 2005;182:161–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
