Increasing the Spatial Resolution of 3T Carotid MRI Has No Beneficial Effect for Plaque Component Measurement Reproducibility
- PMID: 26161783
- PMCID: PMC4498614
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130878
Increasing the Spatial Resolution of 3T Carotid MRI Has No Beneficial Effect for Plaque Component Measurement Reproducibility
Abstract
Purpose: Different in-plane resolutions have been used for carotid 3T MRI. We compared the reproducibility, as well as the within- and between reader variability of high and routinely used spatial resolution in scans of patients with atherosclerotic carotid artery disease. Since no consensus exists about the optimal segmentation method, we analysed all imaging data using two different segmentation methods.
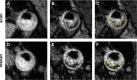
Materials and methods: In 31 patient with carotid atherosclerosis a high (0.25 × 0.25 mm2; HR) and routinely used (0.50 × 0.50 mm2; LR) spatial resolution carotid MRI scan were performed within one month. A fully blinded closed and a simultaneously open segmentation were used to quantify the lipid rich necrotic core (LRNC), calcified and loose matrix (LM) plaque area and the fibrous cap (FC) thickness.
Results: No significant differences were observed between scan-rescan reproducibility for HR versus LR measurements, nor did we find any significant difference between the within-reader and between-reader reproducibility. The same applies for differences between the open and closed reads. All intraclass correlation coefficients between scans and rescans for the LRNC, calcified and LM plaque area, as well as the FC thickness measurements with the open segmentation method were excellent (all above 0.75).
Conclusions: Increasing the spatial resolution at the expense of the contrast-to-noise ratio does not improve carotid plaque component scan-rescan reproducibility in patients with atherosclerotic carotid disease, nor does using a different segmentation method.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Manual versus Automated Carotid Artery Plaque Component Segmentation in High and Lower Quality 3.0 Tesla MRI Scans.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 8;11(12):e0164267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164267. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27930665 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing spatial resolution of 3T MRI scanning improves reproducibility of carotid arterial wall dimension measurements.MAGMA. 2014 Jun;27(3):219-26. doi: 10.1007/s10334-013-0407-2. Epub 2013 Sep 18. MAGMA. 2014. PMID: 24046072
-
Plaque components segmentation in carotid artery on simultaneous non-contrast angiography and intraplaque hemorrhage imaging using machine learning.Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jul;60:93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30959178
-
Contemporary carotid imaging: from degree of stenosis to plaque vulnerability.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):27-42. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26230478 Review.
-
[Dual source computed tomography in analysis of significance and morphology carotid plaques].Przegl Lek. 2013;70(3):118-22. Przegl Lek. 2013. PMID: 24003664 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Manual versus Automated Carotid Artery Plaque Component Segmentation in High and Lower Quality 3.0 Tesla MRI Scans.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 8;11(12):e0164267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164267. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27930665 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Tumor-Specific MRI Biomarkers Using Machine Learning (ML).Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;11(5):742. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050742. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, et al. (2005) Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 366: 1267–1278. - PubMed
-
- Corti R, Fuster V, Fayad ZA, Worthley SG, Helft G, Smith D, et al. (2002) Lipid lowering by simvastatin induces regression of human atherosclerotic lesions: two years’ follow-up by high-resolution noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 106: 2884–2887. - PubMed
-
- Underhill HR, Yuan C, Zhao XQ, Kraiss LW, Parker DL, Saam T, et al. (2008) Effect of rosuvastatin therapy on carotid plaque morphology and composition in moderately hypercholesterolemic patients: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging trial. Am Hear J 155: 584 e1–8. - PubMed
-
- Shinnar M, Fallon JT, Wehrli S, Levin M, Dalmacy D, Fayad ZA, et al. (1999) The diagnostic accuracy of ex vivo MRI for human atherosclerotic plaque characterization. Arter Thromb Vasc Biol 19: 2756–2761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

