Development of Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assays for Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi or Rickettsia typhi
- PMID: 26161793
- PMCID: PMC4498641
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003884
Development of Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assays for Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi or Rickettsia typhi
Abstract
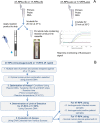
Sensitive, specific and rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi (O. tsutsugamushi) and Rickettsia typhi (R. typhi), the causative agents of scrub typhus and murine typhus, respectively, are necessary to accurately and promptly diagnose patients and ensure that they receive proper treatment. Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assays using a lateral flow test (RPA-nfo) and real-time fluorescent detection (RPA-exo) were developed targeting the 47-kDa gene of O. tsutsugamushi or 17 kDa gene of R. typhi. The RPA assay was capable of detecting O. tsutsugamushi or R. typhi at levels comparable to that of the quantitative PCR method. Both the RPA-nfo and RPA-exo methods performed similarly with regards to sensitivity when detecting the 17 kDa gene of R. typhi. On the contrary, RPA-exo performed better than RPA-nfo in detecting the 47 kDa gene of O. tsutsugamushi. The clinical performance of the O. tsutsugamushi RPA assay was evaluated using either human patient samples or infected mouse samples. Eight out of ten PCR confirmed positives were determined positive by RPA, and all PCR confirmed negative samples were negative by RPA. Similar results were obtained for R. typhi spiked patient sera. The assays were able to differentiate O. tsutsugamushi and R. typhi from other phylogenetically related bacteria as well as mouse and human DNA. Furthermore, the RPA-nfo reaction was completed in 20 minutes at 37°C followed by a 10 minute incubation at room temperature for development of an immunochromatographic strip. The RPA-exo reaction was completed in 20 minutes at 39°C. The implementation of a cross contamination proof cassette to detect the RPA-nfo fluorescent amplicons provided an alternative to regular lateral flow detection strips, which are more prone to cross contamination. The RPA assays provide a highly time-efficient, sensitive and specific alternative to other methods for diagnosing scrub typhus or murine typhus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Walker DH (2007) Rickettsiae and Rickettsial Infections: The Current State of Knowledge. Clin Infec Dis 45: S39–S44. - PubMed
-
- Bavaro MF, Kelly DJ, Dasch DA, Hale BR, Olson P (2005) History of U. S. Military Contributions to the study of Rickettsial Diseases. Military Medicine 170:49–60. - PubMed
-
- Kelly DJ, Richards AL, Temenak J, Strickman D, Dasch GA (2002) The past and present threat of rickettsial diseases to military medicine and international public health, Clinical Infect. Dis. 34: S145–S169. - PubMed
-
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D (2004) Rickettsial infections—a threat to travellers? Curr Opin Infect Dis 17:433–7. - PubMed
-
- Kovacova E, Kazar J (2000) Rickettsial diseases and their serological diagnosis. Clin Lab 46:239–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

