5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Based Sonodynamic Therapy Induces the Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma in Mice
- PMID: 26161801
- PMCID: PMC4498784
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132074
5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Based Sonodynamic Therapy Induces the Apoptosis of Osteosarcoma in Mice
Abstract
Objective: Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is promising for treatment of cancer, but its effect on osteosarcoma is unclear. This study examined the effect of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid (5-ALA)-based SDT on the growth of implanted osteosarcoma and their potential mechanisms in vivo and in vitro.
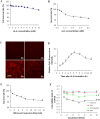
Methods: The dose and metabolism of 5-ALA and ultrasound periods were optimized in a mouse model of induced osteosarcoma and in UMR-106 cells. The effects of ALA-SDT on the proliferation and apoptosis of UMR-106 cells and the growth of implanted osteosarcoma were examined. The levels of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔψM), ROS production, BcL-2, Bax, p53 and caspase 3 expression in UMR-106 cells were determined.
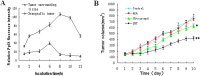
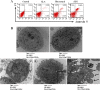
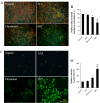
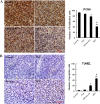
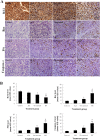
Results: Treatment with 5-ALA for eight hours was optimal for ALA-SDT in the mouse tumor model and treatment with 2 mM 5-ALA for 6 hours and ultrasound (1.0 MHz 2.0 W/cm2) for 7 min were optimal for UMR-106 cells. SDT, but not 5-ALA, alone inhibited the growth of implanted osteosarcoma in mice (P<0.01) and reduced the viability of UMR-106 cells (p<0.05). ALA-SDT further reduced the tumor volumes and viability of UMR-106 cells (p<0.01 for both). Pre-treatment with 5-ALA significantly enhanced the SDT-mediated apoptosis (p<0.01) and morphological changes. Furthermore, ALA-SDT significantly reduced the levels of ΔψM, but increased levels of ROS in UMR-106 cells (p<0.05 or p<0.01 vs. the Control or the Ultrasound). Moreover, ALA-SDT inhibited the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells and BcL-2 expression, but increased levels of Bax, p53 and caspase 3 expression in the implanted osteosarcoma tissues (p<0.05 or p<0.01 vs. the Control or the Ultrasound).
Conclusions: The ALA-SDT significantly inhibited osteosarcoma growth in vivo and reduced UMR-106 cell survival by inducing osteosarcoma cell apoptosis through the ROS-related mitochondrial pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hyperthermotherapy enhances antitumor effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy with activation of caspase-dependent apoptotic pathway in human glioma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):10415-26. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4931-3. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26846106
-
The predominant pathway of apoptosis in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells induced by 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy is the mitochondria-caspase pathway despite the participation of endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(6):1789-801. doi: 10.1159/000362958. Epub 2014 May 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24923653
-
5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Mediated Sonodynamic Therapy Alleviates Atherosclerosis via Enhancing Efferocytosis and Facilitating a Shift in the Th1/Th2 Balance Toward Th2 Polarization.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(1):83-96. doi: 10.1159/000489751. Epub 2018 May 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29763901
-
Sonodynamic therapy, a treatment developing from photodynamic therapy.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2017 Sep;19:159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 10. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2017. PMID: 28606724 Review.
-
Sonodynamic therapy: Ultrasound parameters and in vitro experimental configurations.Int J Pharm. 2021 Dec 15;610:121243. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121243. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34743959 Review.
Cited by
-
MR-guided Focused Ultrasound Facilitates Sonodynamic Therapy with 5-Aminolevulinic Acid in a Rat Glioma Model.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 18;9(1):10465. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46832-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31320671 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-targeted organic sonodynamic therapy agents: concept, benefits, and future directions.Front Chem. 2023 Jun 8;11:1212193. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1212193. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37361020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Focused Ultrasound in Cerebrovascular Diseases and Brain Tumors.Neurotherapeutics. 2019 Jan;16(1):67-87. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-00683-3. Neurotherapeutics. 2019. PMID: 30406382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Focused Ultrasound for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: A New Frontier.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;14(19):4920. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194920. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Assembling Imageable Silk Hydrogels for the Focal Treatment of Osteosarcoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 20;10:698282. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.698282. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35794868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chou AJ, Geller DS, Gorlick R ((2008) Therapy for osteosarcoma: where do we go from here? Paediatr Drugs 10: 315–327. - PubMed
-
- Tian Z, Quan X, Xu C, Dan L, Guo H, Leung W ((2009) Hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether enhances the killing action of ultrasound on osteosarcoma in vivo. J Ultrasound Med 28: 1695–1702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

