Insulin Regulates the Activity of the High-Affinity Choline Transporter CHT
- PMID: 26161852
- PMCID: PMC4498808
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132934
Insulin Regulates the Activity of the High-Affinity Choline Transporter CHT
Abstract
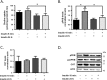
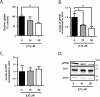
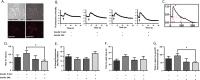
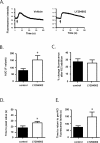
Studies in humans and animal models show that neuronal insulin resistance increases the risk of developing Alzheimer's Disease (AD), and that insulin treatment may promote memory function. Cholinergic neurons play a critical role in cognitive and attentional processing and their dysfunction early in AD pathology may promote the progression of AD pathology. Synthesis and release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) is closely linked to the activity of the high-affinity choline transporter protein (CHT), but the impact of insulin receptor signaling and neuronal insulin resistance on these aspects of cholinergic function are unknown. In this study, we used differentiated SH-SY5Y cells stably-expressing CHT proteins to study the effect of insulin signaling on CHT activity and function. We find that choline uptake activity measured after acute addition of 20 nM insulin is significantly lower in cells that were grown for 24 h in media containing insulin compared to cells grown in the absence of insulin. This coincides with loss of ability to increase phospho-Protein Kinase B (PKB)/Akt levels in response to acute insulin stimulation in the chronic insulin-treated cells. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) in cells significantly lowers phospho-PKB/Akt levels and decreases choline uptake activity. We show total internal reflection microscopy (TIRF) imaging of the dynamic movement of CHT proteins in live cells in response to depolarization and drug treatments. These data show that acute exposure of depolarized cells to insulin is coupled to transiently increased levels of CHT proteins at the cell surface, and that this is attenuated by chronic insulin exposure. Moreover, prolonged inhibition of PI3-kinase results in enhanced levels of CHT proteins at the cell surface by decreasing their rate of internalization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid, transient effects of the protein kinase C activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate on activity and trafficking of the rat high-affinity choline transporter.Neuroscience. 2010 May 19;167(3):765-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.026. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20167259
-
Regulation of the high-affinity choline transporter activity and trafficking by its association with cholesterol-rich lipid rafts.J Neurochem. 2014 Mar;128(5):725-40. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12490. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24127780
-
Differential regulation of the high-affinity choline transporter by wild-type and Swedish mutant amyloid precursor protein.J Neurochem. 2015 Aug;134(4):769-82. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13167. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25970623
-
Modulation of sodium-coupled choline transporter CHT function in health and disease.Neurochem Int. 2020 Nov;140:104810. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104810. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Neurochem Int. 2020. PMID: 32768485 Review.
-
The high-affinity choline transporter: a critical protein for sustaining cholinergic signaling as revealed in studies of genetically altered mice.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(175):525-44. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29784-7_21. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16722248 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction model for mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes using the autonomic function test.Neurol Sci. 2024 Aug;45(8):3757-3766. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07451-6. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38520638
-
The Potential Effect of Insulin on AChE and Its Interactions with Rivastigmine In Vitro.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;14(11):1136. doi: 10.3390/ph14111136. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832918 Free PMC article.
-
Reassessment of Pioglitazone for Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 16;15:666958. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.666958. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34220427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin resistance induces earlier initiation of cognitive dysfunction mediated by cholinergic deregulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Aging Cell. 2023 Nov;22(11):e13994. doi: 10.1111/acel.13994. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 37822109 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Jul 17;20(1):20251225. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1225. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40688037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hasselmo ME, Giocomo LM. Cholinergic modulation of cortical function. J Mol Neurosci. 2006;30:133–5. - PubMed
-
- Ikonomovic MD, Mufson EJ, Wuu J, Cochran EJ, Bennett DA, DeKosky ST. Cholinergic plasticity in hippocampus of individuals with mild cognitive impairment: correlation with Alzheimer's neuropathology. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2003;5:39–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

