Flot-2 Expression Correlates with EGFR Levels and Poor Prognosis in Surgically Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26161893
- PMCID: PMC4498790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132190
Flot-2 Expression Correlates with EGFR Levels and Poor Prognosis in Surgically Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
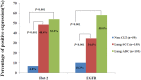
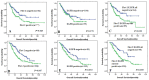
We previously reported that expression of Flotillin 2 (Flot-2), a protein isolated from caveolae/lipid raft domains, increased significantly in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) compared with normal tissues. Signal transduction through epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) and Flot-2 play an important role in cancer development, but their precise role in lung cancer has not been investigated. In this study, we have investigated the correlation between the expression of Flot-2 and EGFR, which increase significantly in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (n=352) compared with non-cancer tissues. Additionally, patients with advanced stages of NSCLC had higher positive expression of Flot-2 and EGFR than patients with early stages. NSCLC patients with increased expression of Flot-2 and EGFR had significantly less overall survival rates than patients with less expression of Flot-2 and EGFR. Taken together, our data suggest that increased expression of Flot-2 and EGFR in NSCLC patients is inversely proportional to the disease prognosis and that increased expression of Flot-2 associated with increased EGFR may serve as a biomarker to predict poor disease prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
High coexpression of both EGFR and IGF1R correlates with poor patient prognosis in resected non-small-cell lung cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2014 Jan;15(1):58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Clin Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24210543
-
Prognostic significance of MCM7 expression in the bronchial brushings of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2012 Jul;77(1):176-82. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 26. Lung Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22456526
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and the epidermal growth factor signal pathway in operable non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Jun;6(6):2349-55. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10873086
-
[Expression and clinical significance of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 8 (ADAM8) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in non-small cell lung cancer].Ai Zheng. 2008 Aug;27(8):874-8. Ai Zheng. 2008. PMID: 18710625 Chinese.
-
[Epidermal growth factor receptors and their ligands in non-small-cell lung carcinoma].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 1998;(5):51-4. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 1998. PMID: 9662999 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Elevated expression of G3BP1 associates with YB1 and p-AKT and predicts poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients after surgical resection.Cancer Med. 2019 Nov;8(16):6894-6903. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2579. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31560169 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-150-3p enhances the antitumour effects of CGP57380 and is associated with a favourable prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):1973. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85793-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39809860 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-mediated miR-7-5p delivery enhances the anticancer effect of Everolimus via blocking MNK/eIF4E axis in non-small cell lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 8;13(2):129. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04565-7. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35136028 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of FAT4 suppress metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma through regulating MAPK pathway and associated with immune cells infiltration.Cancer Med. 2023 Jan;12(2):1616-1629. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4977. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35770846 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of P4HA1 associates with poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Sep 21;12(22):6685-6694. doi: 10.7150/jca.63147. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34659558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bickel PE, Scherer PE, Schnitzer JE, Oh P, Lisanti MP, Lodish HF. Flotillin and epidermal surface antigen define a new family of caveolae-associated integral membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272: 13793–13802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

