Using Whole Genome Analysis to Examine Recombination across Diverse Sequence Types of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 26161978
- PMCID: PMC4498916
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130955
Using Whole Genome Analysis to Examine Recombination across Diverse Sequence Types of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
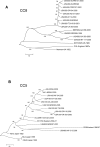
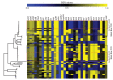
Staphylococcus aureus is an important clinical pathogen worldwide and understanding this organism's phylogeny and, in particular, the role of recombination, is important both to understand the overall spread of virulent lineages and to characterize outbreaks. To further elucidate the phylogeny of S. aureus, 35 diverse strains were sequenced using whole genome sequencing. In addition, 29 publicly available whole genome sequences were included to create a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based phylogenetic tree encompassing 11 distinct lineages. All strains of a particular sequence type fell into the same clade with clear groupings of the major clonal complexes of CC8, CC5, CC30, CC45 and CC1. Using a novel analysis method, we plotted the homoplasy density and SNP density across the whole genome and found evidence of recombination throughout the entire chromosome, but when we examined individual clonal lineages we found very little recombination. However, when we analyzed three branches of multiple lineages, we saw intermediate and differing levels of recombination between them. These data demonstrate that in S. aureus, recombination occurs across major lineages that subsequently expand in a clonal manner. Estimated mutation rates for the CC8 and CC5 lineages were different from each other. While the CC8 lineage rate was similar to previous studies, the CC5 lineage was 100-fold greater. Fifty known virulence genes were screened in all genomes in silico to determine their distribution across major clades. Thirty-three genes were present variably across clades, most of which were not constrained by ancestry, indicating horizontal gene transfer or gene loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Jevons M. “Celbenin” - resistant Staphylococci. Br Med J. 1961;1:124–5. doi: 10.1136/bmj. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

