Drosophila anti-nematode and antibacterial immune regulators revealed by RNA-Seq
- PMID: 26162375
- PMCID: PMC4499211
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-1690-2
Drosophila anti-nematode and antibacterial immune regulators revealed by RNA-Seq
Abstract
Background: Drosophila melanogaster activates a variety of immune responses against microbial infections. However, information on the Drosophila immune response to entomopathogenic nematode infections is currently limited. The nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora is an insect parasite that forms a mutualistic relationship with the gram-negative bacteria Photorhabdus luminescens. Following infection, the nematodes release the bacteria that quickly multiply within the insect and produce several toxins that eventually kill the host. Although we currently know that the insect immune system interacts with Photorhabdus, information on interaction with the nematode vector is scarce.
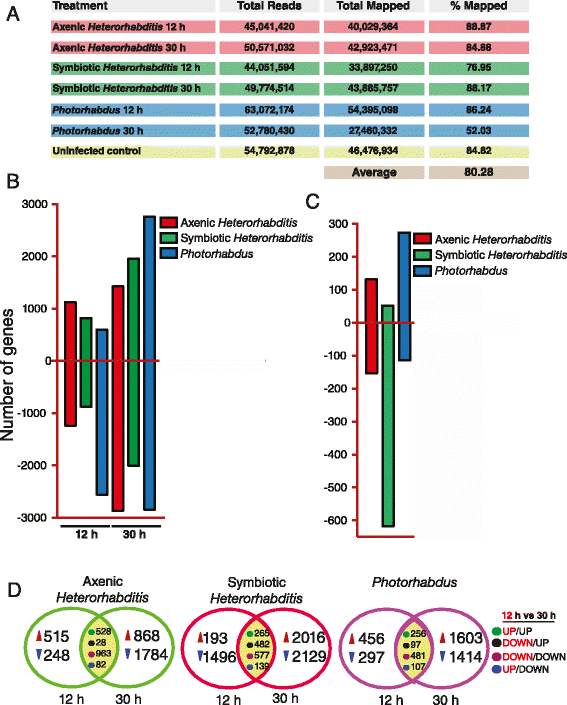
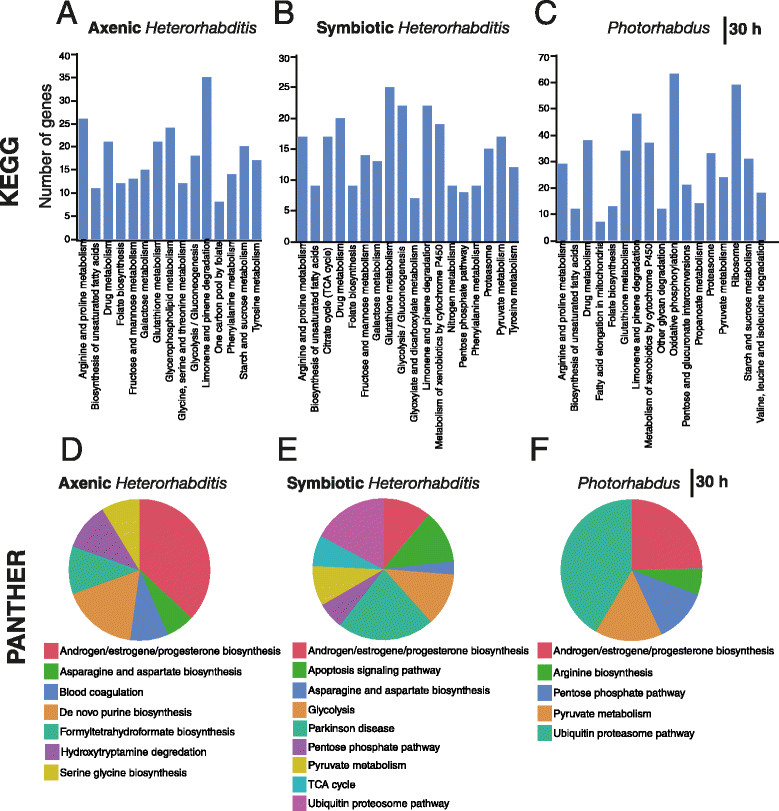
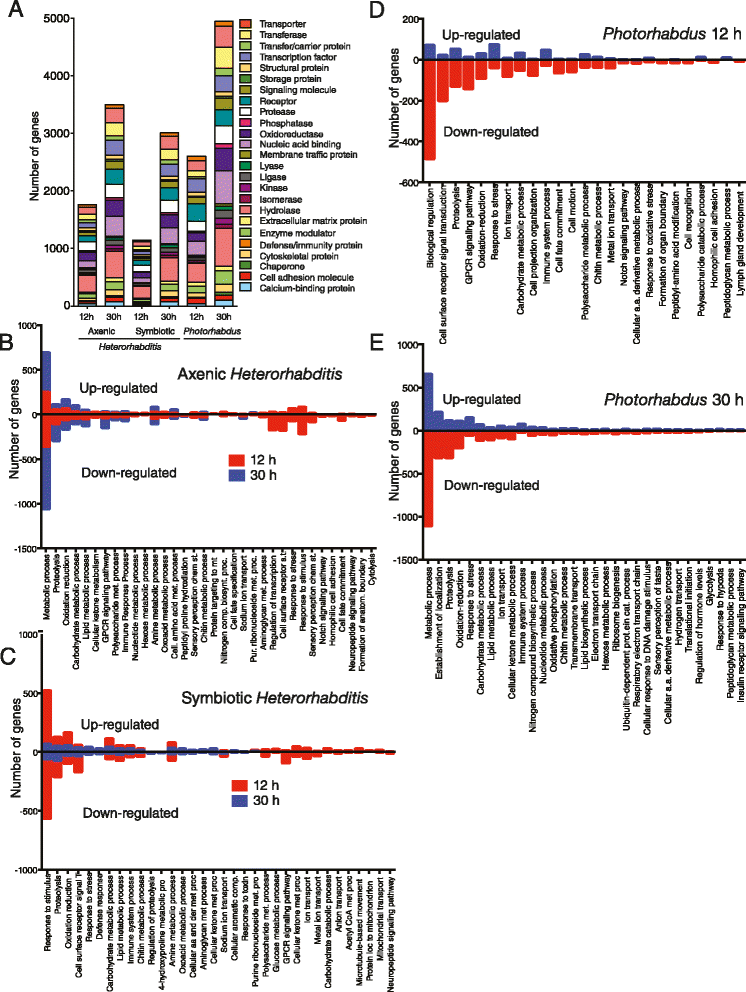
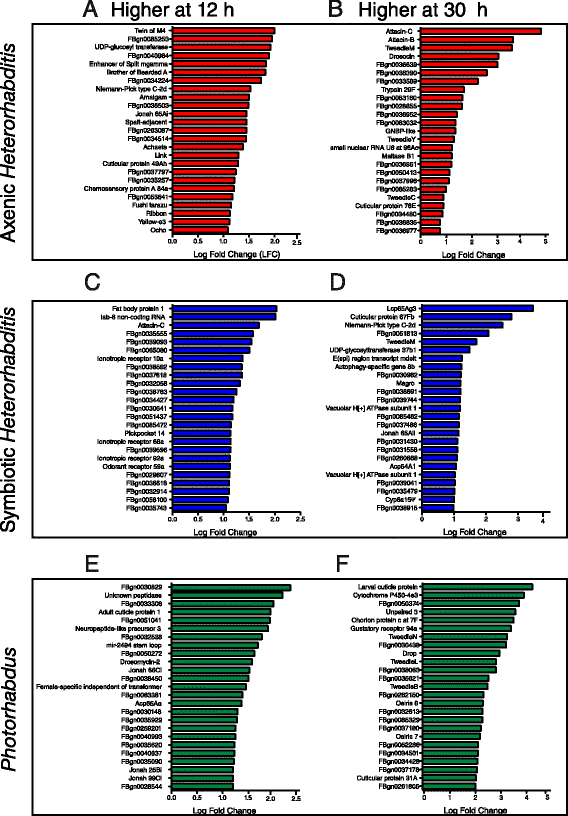
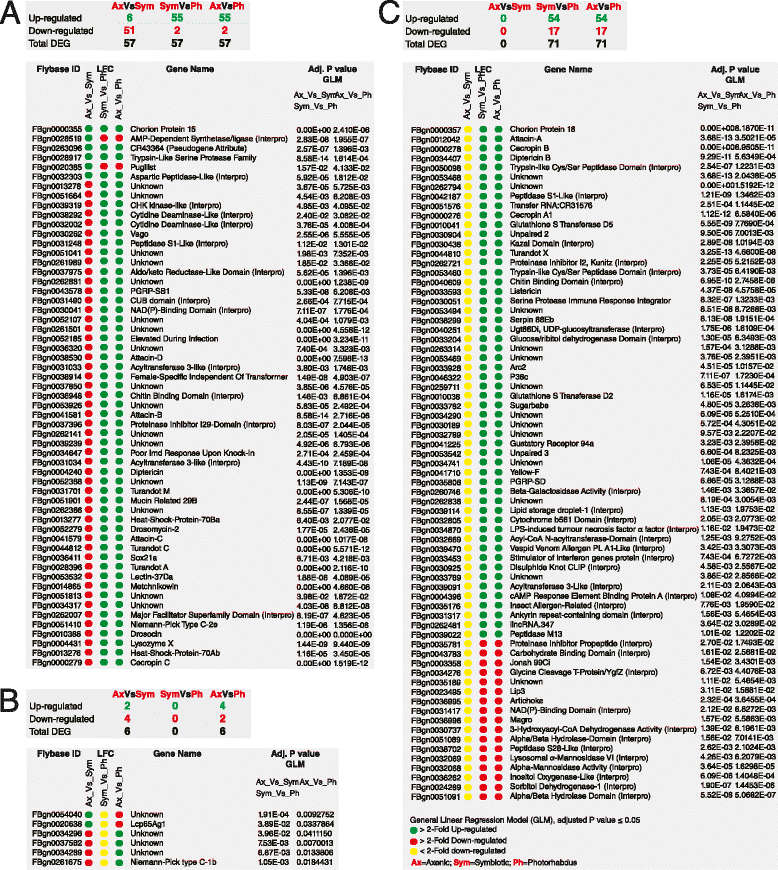
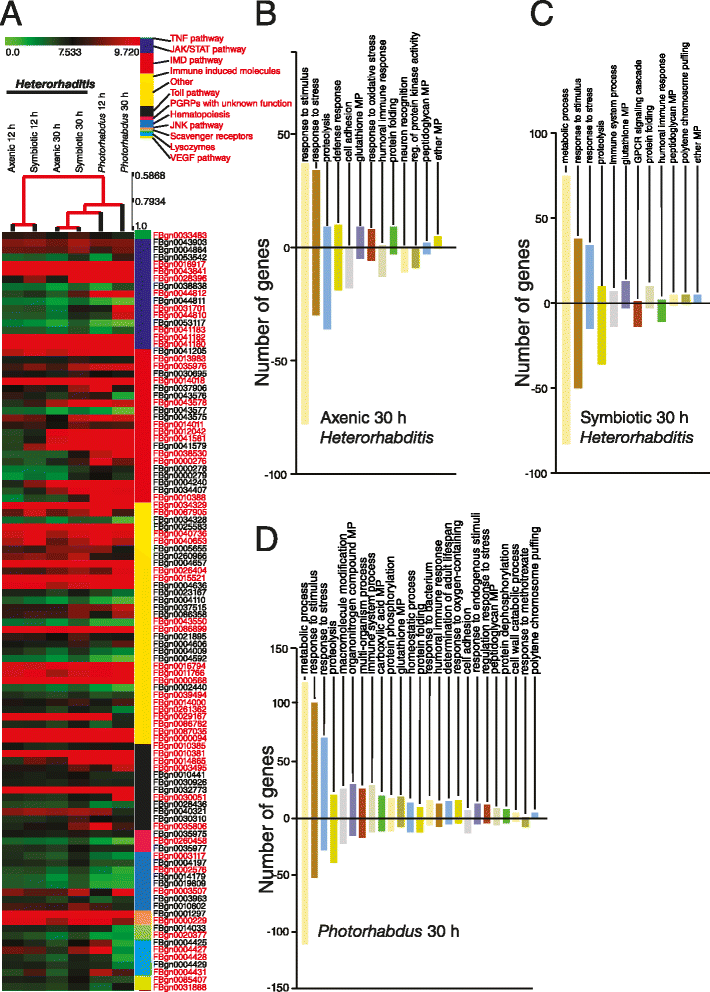
Results: Here we have used next generation RNA-sequencing to analyze the transcriptional profile of wild-type adult flies infected by axenic Heterorhabditis nematodes (lacking Photorhabdus bacteria), symbiotic Heterorhabditis nematodes (carrying Photorhabdus bacteria), and Photorhabdus bacteria alone. We have obtained approximately 54 million reads from the different infection treatments. Bioinformatic analysis shows that infection with Photorhabdus alters the transcription of a large number of Drosophila genes involved in translational repression as well in response to stress. However, Heterorhabditis infection alters the transcription of several genes that participate in lipidhomeostasis and metabolism, stress responses, DNA/protein synthesis and neuronal functions. We have also identified genes in the fly with potential roles in nematode recognition, anti-nematode activity and nociception.
Conclusions: These findings provide fundamental information on the molecular events that take place in Drosophila upon infection with the two pathogens, either separately or together. Such large-scale transcriptomic analyses set the stage for future functional studies aimed at identifying the exact role of key factors in the Drosophila immune response against nematode-bacteria complexes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune gene transcription in Drosophila adult flies infected by entomopathogenic nematodes and their mutualistic bacteria.J Insect Physiol. 2013 Feb;59(2):179-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 17. J Insect Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22902989
-
Dynamics of transcriptomic response to infection by the nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora and its bacterial symbiont Photorhabdus temperata in Heliothis virescens larvae.Insect Mol Biol. 2017 Oct;26(5):584-600. doi: 10.1111/imb.12321. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Insect Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28640534
-
Activin and BMP Signaling Activity Affects Different Aspects of Host Anti-Nematode Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:795331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.795331. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003118 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Insights into the Insect Immune Response to Nematode Infection.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;12(2):202. doi: 10.3390/genes12020202. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33573306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nematode infection and antinematode immunity in Drosophila.Trends Parasitol. 2021 Nov;37(11):1002-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Trends Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34154933 Review.
Cited by
-
Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Regulate Host Immune Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae.Insects. 2024 Jul 9;15(7):514. doi: 10.3390/insects15070514. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39057246 Free PMC article.
-
Thioester-containing proteins in the tsetse fly (Glossina) and their response to trypanosome infection.Insect Mol Biol. 2018 Jun;27(3):414-428. doi: 10.1111/imb.12382. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Insect Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29528164 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression in skin RNA of horses affected with degenerative suspensory ligament desmitis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Oct 7;15(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01994-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33028365 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal diet affects differential gene expression, but not sperm competition, in sons.Biol Lett. 2017 Feb;13(2):20160914. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2016.0914. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Biol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28202685 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional up-regulation of the TGF-β intracellular signaling transducer Mad of Drosophila larvae in response to parasitic nematode infection.Innate Immun. 2018 Aug;24(6):349-356. doi: 10.1177/1753425918790663. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Innate Immun. 2018. PMID: 30049242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brivio MF, Mastore M, Pagani M. Parasite-host relationship: a lesson from a professional killer. Invertebr Surv J. 2005;2:41–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

