Echocardiographic Findings Predict In-Hospital and 1-Year Mortality in Left-Sided Native Valve Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis: Analysis From the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Echo Cohort Study
- PMID: 26162783
- PMCID: PMC4503384
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.114.003397
Echocardiographic Findings Predict In-Hospital and 1-Year Mortality in Left-Sided Native Valve Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis: Analysis From the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Echo Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus left-sided native valve infective endocarditis (LNVIE) has higher complication and mortality rates compared with endocarditis from other pathogens. Whether echocardiographic variables can predict prognosis in S aureus LNVIE is unknown.
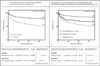
Methods and results: Consecutive patients with LNVIE, enrolled between January 2000 and September 2006, in the International Collaboration on Endocarditis were identified. Subjects without S aureus IE were matched to those with S aureus IE by the propensity of having S aureus. Survival differences were determined using log-rank significance tests. Independent echocardiographic predictors of mortality were identified using Cox-proportional hazards models that included inverse probability of treatment weighting and surgery as a time-dependent covariate. Of 727 subjects with LNVIE and 1-year follow-up, 202 had S aureus IE. One-year survival rates were significantly lower for patients with S aureus IE overall (57% S aureus IE versus 80% non-S aureus IE; P<0.001) and in the propensity-matched cohort (59% S aureus IE versus 68% non-S aureus IE; P<0.05). Intracardiac abscess (hazard ratio, 2.93; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-5.40; P<0.001) and left ventricular ejection fraction <40% (odds ratio, 3.01; 95% confidence interval, 1.35-6.04; P=0.004) were the only independent echocardiographic predictors of in-hospital mortality in S aureus LNVIE. Valve perforation (hazard ratio, 2.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-3.68; P=0.006) and intracardiac abscess (hazard ratio, 2.25; 95% confidence interval, 1.26-3.78; P=0.004) were the only independent predictors of 1-year mortality.
Conclusions: S aureus is an independent predictor of 1-year mortality in subjects with LNVIE. In S aureus LNVIE, intracardiac abscess and left ventricular ejection fraction <40% independently predicted in-hospital mortality and intracardiac abscess and valve perforation independently predicted 1-year mortality.
Keywords: echocardiography; endocarditis; odds ratio; risk factors; survival analysis.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures

Comment in
-
Prognostic Assessment of Infective Endocarditis Using Echocardiography: What Is New?Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Jul;8(7):e003791. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003791. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26162784 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Two-dimensional global longitudinal strain is superior to left ventricular ejection fraction in prediction of outcome in patients with left-sided infective endocarditis.Int J Cardiol. 2018 Jun 1;260:118-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.01.031. Int J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29622424
-
Clinical characteristics and outcome of aortic endocarditis with periannular abscess in the International Collaboration on Endocarditis Merged Database.Am J Cardiol. 2005 Oct 1;96(7):976-81. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.05.056. Am J Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 16188527
-
Staphylococcus lugdunensis infective endocarditis: description of 10 cases and analysis of native valve, prosthetic valve, and pacemaker lead endocarditis clinical profiles.Heart. 2005 Feb;91(2):e10. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2004.040659. Heart. 2005. PMID: 15657200 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus lugdunensis infective endocarditis: a literature review and analysis of risk factors.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2010 Dec;43(6):478-84. doi: 10.1016/S1684-1182(10)60074-6. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2010. PMID: 21195974 Review.
-
The role of transesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of patients with aortic perivalvular abscesses.Am J Med Sci. 2001 Feb;321(2):152-5. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200102000-00007. Am J Med Sci. 2001. PMID: 11271750 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus increases platelet reactivity in patients with infective endocarditis.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 28;12(1):12933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16681-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35902612 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic predictors and associated outcomes of multiple vegetations in infective endocarditis: A pilot study.World J Cardiol. 2024 Jun 26;16(6):318-328. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i6.318. World J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38993586 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and long-term outcomes in infective endocarditis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Dec 12;17(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0729-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 29233094 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between echocardiographic manifestations and bacterial species in patients with infective endocarditis: a cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Dec 16;19(1):1052. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4682-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31842764 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing a hospital-wide protocol for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Aug;37(8):1553-1562. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3284-9. Epub 2018 May 31. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29855842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fowler VG, Jr, Miro JM, Hoen B, Cabell CH, Abrutyn E, Rubinstein E, Corey GR, Spelman D, Bradley SF, Barsic B, Pappas PA, Anstrom KJ, Wray D, Fortes CQ, Anguera I, Athan E, Jones P, van der Meer JT, Elliott TS, Levine DP, Bayer AS. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: a consequence of medical progress. JAMA. 2005;293:3012–3021. - PubMed
-
- Murdoch DR, Corey GR, Hoen B, Miró JM, Fowler VG, Jr, Bayer AS, Karchmer AW, Olaison L, Pappas PA, Moreillon P, Chambers ST, Chu VH, Falcó V, Holland DJ, Jones P, Klein JL, Raymond NJ, Read KM, Tripodi MF, Utili R, Wang A, Woods CW, Cabell CH. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century:the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:463–473. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rizzi M, Ravasio V, Carobbio A, Mattucci I, Crapis M, Stellini R, Pasticci MB, Chinello P, Falcone M, Grossi P, Barbaro F, Pan A, Viale P, Durante-Mangoni E. Predicting the occurrence of embolic events: an analysis of 1456 episodes of infective endocarditis from the Italian Study on Endocarditis. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:230–235. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thuny F, Di Salvo G, Belliard O, Avierinos JF, Pergola V, Rosenberg V, Casalta JP, Gouvernet J, Derumeaux G, Iarussi D, Ambrosi P, Calabró R, Riberi A, Collart F, Metras D, Lepidi H, Raoult D, Harle JR, Weiller PJ, Cohen A, Habib G. Risk of embolism and death in infective endocarditis:prognostic value of echocardiography:a prospective multicenter study. Circulation. 2005;112:69–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

