Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing for treating psychological disturbances in Taiwanese adolescents who experienced Typhoon Morakot
- PMID: 26162817
- PMCID: PMC11916063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.04.013
Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing for treating psychological disturbances in Taiwanese adolescents who experienced Typhoon Morakot
Abstract
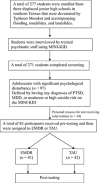
In this case-control study, we aimed to assess the intervention effects of four-session eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) on reducing the severity of disaster-related anxiety, general anxiety, and depressive symptoms in Taiwanese adolescents who experienced Typhoon Morakot. A total of 83 adolescents with posttraumatic stress disorder related to Typhoon Morakot, major depressive disorder, or current moderate or high suicide risk after experiencing Typhoon Morakot were allocated to a four-session course of EMDR (N = 41) or to treatment as usual (TAU; N = 42). A multivariate analysis of covariance was performed to examine the effects of EMDR in reducing the severity of disaster-related anxiety, general anxiety, and depressive symptoms in adolescents by using preintervention severity values as covariates. The multivariate analysis of covariance results indicated that the EMDR group exhibited significantly lower preintervention severity values of general anxiety and depression than did the TAU group. In addition, the preintervention severity value of disaster-related anxiety in the EMDR group was lower than that in the TAU group (p = 0.05). The results of this study support that EMDR could alleviate general anxiety and depressive symptoms and reduce disaster-related anxiety in adolescents experiencing major traumatic disasters.
Keywords: Adolescent; Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing; Major depressive disorder; Posttraumatic stress disorder.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Taiwan.
Similar articles
-
Eye movement desensitization and processing for adolescents with major depressive disorder: study protocol for a multi-site randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2023 Mar 20;24(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07226-y. Trials. 2023. PMID: 36941688 Free PMC article.
-
Suicide risk and its correlate in adolescents who experienced typhoon-induced mudslides: a structural equation model.Depress Anxiety. 2010 Dec;27(12):1143-8. doi: 10.1002/da.20748. Depress Anxiety. 2010. PMID: 21049526
-
Early intervention with eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy to reduce the severity of post-traumatic stress symptoms in recent rape victims: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2021 Sep 9;12(1):1943188. doi: 10.1080/20008198.2021.1943188. eCollection 2021. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2021. PMID: 34531963 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Psychological therapies for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents (Review).Evid Based Child Health. 2013 May;8(3):1004-116. doi: 10.1002/ebch.1916. Evid Based Child Health. 2013. PMID: 23877914 Review.
-
25 years of Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): The EMDR therapy protocol, hypotheses of its mechanism of action and a systematic review of its efficacy in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder.Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment (Engl Ed). 2018 Apr-Jun;11(2):101-114. doi: 10.1016/j.rpsm.2015.12.002. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 26877093 Review. English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing Treatment for Depression: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 23;13(18):5633. doi: 10.3390/jcm13185633. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39337119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dealing With the Aftermath of Mass Disasters: A Field Study on the Application of EMDR Integrative Group Treatment Protocol With Child Survivors of the 2016 Italy Earthquakes.Front Psychol. 2018 Jun 4;9:862. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00862. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29915550 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Interventions for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder as a Primary Diagnosis Among Adolescents: A Meta-analysis.Indian J Psychol Med. 2024 Jun 13:02537176241255643. doi: 10.1177/02537176241255643. Online ahead of print. Indian J Psychol Med. 2024. PMID: 39564348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Scoping Review of Trauma-Informed Pediatric Interventions in Response to Natural and Biologic Disasters.Children (Basel). 2023 Jun 5;10(6):1017. doi: 10.3390/children10061017. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371249 Free PMC article.
-
Depression in Youth Exposed to Disasters, Terrorism and Political Violence.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019 Jul 4;21(8):73. doi: 10.1007/s11920-019-1061-9. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019. PMID: 31270638 Review.
References
-
- Kristensen P., Weisaeth L., Heir T.. Psychiatric disorders among disaster bereaved: an interview study of individuals directly or not directly exposed to the 2004 tsunami. Depress Anxiety. 2009; 26: 1127–1133. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z.Y., Yang Y.F., Ye Y.L., Zeng Z.Q., Xiang Y.J., Yuan P.. One‐year follow‐up study of post‐traumatic stress disorder among adolescents following the Wen‐Chuan earthquake in China. Biosci Trends. 2010; 4: 96–102. - PubMed
-
- Lindal E., Stefansson J.G.. The long‐term psychological effect of fatal accidents at sea on survivors: a cross‐sectional study of North‐Atlantic seamen. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2011; 46: 239–246. - PubMed
-
- Bolton D., O'Ryan D., Udwin O., Boyle S., Yule W.. The long‐term psychological effects of a disaster experienced in adolescence: II. General psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2000; 41: 513–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical