Evaluation of the pharmacological activities of RAD1901, a selective estrogen receptor degrader
- PMID: 26162914
- PMCID: PMC4545300
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-15-0287
Evaluation of the pharmacological activities of RAD1901, a selective estrogen receptor degrader
Abstract
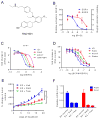
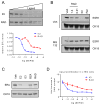
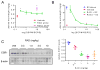
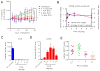
Endocrine therapy, using tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor, remains a first-line treatment for estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) positive breast cancer. However, tumor resistance limits the duration of response. The clinical efficacy of fulvestrant, a selective ER degrader (SERD) that triggers receptor degradation, has confirmed that ESR1 often remains engaged in endocrine therapy resistant cancers. Recently developed, selective ER modulators (SERMs)/SERD hybrids (SSHs) that facilitate ESR1 degradation in breast cancer cells and reproductive tissues have been advanced as an alternative treatment for advanced breast cancer, particularly in the metastatic setting. RAD1901 is one SSH currently being evaluated clinically that is unique among ESR1 modulators in that it readily enters the brain, a common site of breast cancer metastasis. In this study, RAD1901 inhibited estrogen activation of ESR1 in vitro and in vivo, inhibited estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation and xenograft tumor growth, and mediated dose-dependent downregulation of ESR1 protein. However, doses of RAD1901 insufficient to induce ESR1 degradation were shown to result in the activation of ESR1 target genes and in the stimulation of xenograft tumor growth. RAD1901 is an SSH that exhibits complex pharmacology in breast cancer models, having dose-dependent agonist/antagonist activity displayed in a tissue-selective manner. It remains unclear how this unique pharmacology will impact the utility of RAD1901 for breast cancer treatment. However, being the only SERD currently known to access the brain, RAD1901 merits evaluation as a targeted therapy for the treatment of breast cancer brain metastases.
Keywords: RAD1901; SERM; endocrine-resistant breast cancer; selective estrogen receptor degrader.
© 2015 Society for Endocrinology.
Conflict of interest statement
D.P.M. has previously served as a scientific advisory board member for Radius Pharmaceuticals, Inc. D.P.M., S.E.W., and E.R.N. have applied for a patent for the use of RAD1901 for the treatment of breast cancer brain metastases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of SERD/SERM Hybrid-CDK4/6 Inhibitor Combinations in Models of Endocrine Therapy-Resistant Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5121-5130. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0360. Epub 2015 May 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25991817 Free PMC article.
-
RAD1901: a novel, orally bioavailable selective estrogen receptor degrader that demonstrates antitumor activity in breast cancer xenograft models.Anticancer Drugs. 2015 Oct;26(9):948-56. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000271. Anticancer Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26164151 Free PMC article.
-
GLL398, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), blocks tumor growth in xenograft breast cancer models.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Apr;180(2):359-368. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05558-w. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32030569 Free PMC article.
-
The race to develop oral SERDs and other novel estrogen receptor inhibitors: recent clinical trial results and impact on treatment options.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022 Dec;41(4):975-990. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10066-y. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022. PMID: 36229710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel oral selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) to target hormone receptor positive breast cancer: elacestrant as the poster-child.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024 Jun;24(6):397-405. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2024.2346188. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38642015 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic resistance to anti-oestrogen therapy in breast cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2023 Oct;23(10):673-685. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00604-3. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37500767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine resistance in breast cancer: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Dec;99(12):1691-1710. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02136-5. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34623477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nexus between PI3K/AKT and Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 20;13(3):369. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030369. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dysregulated Pharmacology of Clinically Relevant ESR1 Mutants is Normalized by Ligand-activated WT Receptor.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Jul;19(7):1395-1405. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-1148. Epub 2020 May 7. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32381587 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Estrogen Receptor-Targeted Agents for Breast Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023 Jul;24(7):821-844. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01079-y. Epub 2023 May 2. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37129836 Review.
References
-
- Bentrem DJ, Dardes RC, Liu H, Maccgregor-Schafer J, Zapf JW, Jordan VC. Molecular mechanism of action at estrogen receptor alpha of a new clinically relevant antiestrogen (GW7604) related to tamoxifen. Endocrinology. 2001;142:838–846. - PubMed
-
- Carter D. New global survey shows an increasing cancer burden. American Journal of Nursing. 2014;114:17. - PubMed
-
- Chia S, Gradishar W, Mauriac L, Bines J, Amant F, Federico M, Fein L, Romieu G, Buzdar A, Robertson J, et al. Double-blind, randomized placebo controlled trial of Fulvestrant compared with exemestane after prior nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer: results from EFECT. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:1664–1670. - PubMed
-
- Connor CE, Norris JD, Broadwater G, Willson TM, Gottardis MM, Dewhirst MW, McDonnell DP. Circumventing tamoxifen resistance in breast cancers using antiestrogens that induce unique conformational changes in the estrogen receptor. Cancer Research. 2001;61:2917–2922. - PubMed
-
- Dallenbach-Hellweg G, Schmidt D, Hellberg P, Bourne T, Kreuzwieser E, Doren M, Rydh W, Rudenstam G, Granberg S. The endometrium in breast cancer patients on tamoxifen. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics. 2000;263:170–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

