Propofol Protects Against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury in Differentiated PC12 Cells via Inhibition of Ca(2+)-Dependent NADPH Oxidase
- PMID: 26162968
- PMCID: PMC11482435
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-015-0235-1
Propofol Protects Against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury in Differentiated PC12 Cells via Inhibition of Ca(2+)-Dependent NADPH Oxidase
Abstract
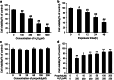
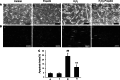
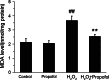
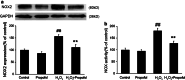
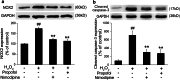
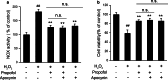
Propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol) is a widely used general anesthetic with anti-oxidant activities. This study aims to investigate protective capacity of propofol against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative injury in neural cells and whether the anti-oxidative effects of propofol occur through a mechanism involving the modulation of NADPH oxidase (NOX) in a manner of calcium-dependent. The rat differentiated PC12 cell was subjected to H2O2 exposure for 24 h to mimic a neuronal in vitro model of oxidative injury. Our data demonstrated that pretreatment of PC12 cells with propofol significantly reversed the H2O2-induced decrease in cell viability, prevented H2O2-induced morphological changes, and reduced the ratio of apoptotic cells. We further found that propofol attenuated the accumulation of malondialdehyde (biomarker of oxidative stress), counteracted the overexpression of NOX core subunit gp91(phox) (NOX2) as well as the NOX activity following H2O2 exposure in PC12 cells. In addition, blocking of L-type Ca(2+) channels with nimodipine reduced H2O2-induced overexpression of NOX2 and caspase-3 activation in PC12 cells. Moreover, NOX inhibitor apocynin alone or plus propofol neither induces a significant downregulation of NOX activity nor increases cell viability compared with propofol alone in the PC12 cells exposed to H2O2. These results demonstrate that the protective effects of propofol against oxidative injury in PC12 cells are mediated, at least in part, through inhibition of Ca(2+)-dependent NADPH oxidase.
Keywords: Hydrogen peroxide; NADPH oxidase; Oxidative injury; PC12 cells; Propofol.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine Protects Against Chemical Hypoxia-Induced Neurotoxicity in Differentiated PC12 Cells Via Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase 2-Mediated Oxidative Stress.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):139-149. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9938-7. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30112693
-
Protective effect of vitexin compound B-1 against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in differentiated PC12 cells via NADPH oxidase inhibition.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;387(9):861-71. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-1006-0. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24947869
-
Studying neuroprotective effect of Atorvastatin as a small molecule drug on high glucose-induced neurotoxicity in undifferentiated PC12 cells: role of NADPH oxidase.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Feb;32(1):41-49. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9883-1. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 27476541 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol Attenuates Small Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury through Inhibiting NADPH Oxidase Mediated Mast Cell Activation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:167014. doi: 10.1155/2015/167014. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26246867 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of phillyrin on H2O 2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in PC12 cells.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Nov;34(8):1165-73. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0091-4. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25146667 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine Protects Against Chemical Hypoxia-Induced Neurotoxicity in Differentiated PC12 Cells Via Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase 2-Mediated Oxidative Stress.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):139-149. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9938-7. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30112693
-
Protective effect of propofol on hydrogen peroxide-induced human esophageal carcinoma via blocking the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Dec;21(12):1297-1304. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.29141.7039. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30627375 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of ROS-mediated activation Src-MAPK/AKT signaling by orientin alleviates H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Nov 16;12:3973-3984. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S178217. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30510405 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol protects human cardiac cells against chemical hypoxiainduced injury by regulating the JNK signaling pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Mar;19(3):1864-1870. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8440. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32104242 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine Alleviates Hypoxia-Induced Synaptic Loss and Cognitive Impairment via Inhibition of Microglial NOX2 Activation in the Hippocampus of Neonatal Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Feb 12;2021:6643171. doi: 10.1155/2021/6643171. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33628369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adembri C, Venturi L, Tani A, Chiarugi A, Gramigni E, Cozzi A, Pancani T, De Gaudio RA, Pellegrini-Giampietro DE (2006) Neuroprotective effects of propofol in models of cerebral ischemia—inhibition of mitochondrial swelling as a possible mechanism. Anesthesiology 104(1):80–89. doi:10.1097/00000542-200601000-00014 - PubMed
-
- Behrens MM, Ali SS, Dao DN, Lucero J, Shekhtman G, Quick KL, Dugan LL (2007) Ketamine-induced loss of phenotype of fast-spiking interneurons is mediated by NADPH-oxidase. Science 318(5856):1645–1647. doi:10.1126/science.1148045 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

