Assessment of the Chinese Resident Health Literacy Scale in a population-based sample in South China
- PMID: 26163383
- PMCID: PMC4498512
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1958-0
Assessment of the Chinese Resident Health Literacy Scale in a population-based sample in South China
Abstract
Background: A national health literacy scale was developed in China in 2012, though no studies have validated it. In this investigation, we assessed the reliability, construct validity, and measurement invariance of that scale.
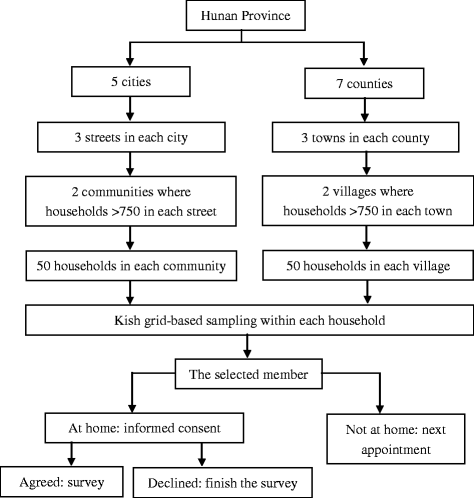
Methods: A population-based sample of 3731 participants in Hunan Province was used to validate the Chinese Resident Health Literacy Scale based on item response theory and classical test theory (including split-half coefficient, Cronbach's alpha, and confirmatory factor analysis). Measurement invariance was examined by differential item functioning.
Results: The overall Cronbach's alpha of the scale was 0.95 and Spearman-Brown coefficient 0.94. Confirmatory factor analysis showed that the test measured a unidimensional construct with three highly correlated factors. Highest discrimination was found among participants with limited to moderate health literacy. In all, 64 items were selected from the original scale based on factor loading, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and discrimination and difficulty parameters in item response theory. Measurement invariance was significant but slight. According to the two-level linear model, health literacy was associated with education level, occupation, and income.
Conclusions: The 2012 national health literacy scale was validated, and 64 items were selected based on classical test theory and item response theory. The revised version of the scale has strong psychometric properties with minor measurement invariance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chinese health literacy scale for tuberculosis patients: a study on development and psychometric testing.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 20;19(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4168-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31221099 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of the Hungarian version of the eHealth Literacy Scale.Eur J Health Econ. 2019 Jun;20(Suppl 1):57-69. doi: 10.1007/s10198-019-01062-1. Epub 2019 May 16. Eur J Health Econ. 2019. PMID: 31098883 Free PMC article.
-
Revised Chinese resident health literacy scale for the older adults in China: simplified version and initial validity testing.Front Public Health. 2023 May 17;11:1147862. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1147862. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37265518 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Establishment of nutrition literacy core items for Chinese old people].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 6;54(10):1075-1080. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200327-00451. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33115192 Review. Chinese.
-
[Establishment of nutrition literacy core items for Chinese people].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 6;54(10):1069-1074. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200327-00458. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33115191 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Serum Folate Shows an Inverse Association with Blood Pressure in a Cohort of Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: A Cross-Sectional Study.PLoS One. 2016 May 16;11(5):e0155801. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155801. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27182603 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Evaluation of the Quality of Life Scale for Children With Visual Impairments in China.Front Pediatr. 2022 Mar 21;10:739296. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.739296. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35386258 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring health literacy in Wuhan, China: a cross-sectional analysis.BMC Public Health. 2020 Sep 17;20(1):1417. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09520-9. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32943017 Free PMC article.
-
Inequalities in the health survey using validation question to filter insufficient effort responding: reducing overestimated effects or creating selection bias?Int J Equity Health. 2019 Aug 22;18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12939-019-1030-2. Int J Equity Health. 2019. PMID: 31438952 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of School-Based Quasi-Experimental Nutrition and Food Safety Health Education for Primary School Students in Two Poverty-Stricken Counties of West China.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0145090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145090. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Ministry of Health . 66 tips of health: Chinese resident health literacy manual. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2008.
-
- Li XH. Brief introduction on identification and dissemination of the Basic Knowledge and Skill of People’s Health Literacy by Chinese government. Chinese J Health Educ. 2008;24(5):385–388.
-
- World Health Organization . Health promotion glossary. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998.
-
- Institute of Medicine . Health literacy: a prescription to end confusion. Washington DC: National Academies Press; 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

