NO to cancer: The complex and multifaceted role of nitric oxide and the epigenetic nitric oxide donor, RRx-001
- PMID: 26164533
- PMCID: PMC4529402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.002
NO to cancer: The complex and multifaceted role of nitric oxide and the epigenetic nitric oxide donor, RRx-001
Abstract
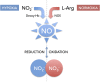
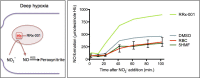
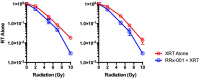
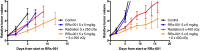
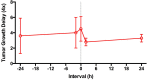
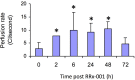
The endogenous mediator of vasodilation, nitric oxide (NO), has been shown to be a potent radiosensitizer. However, the underlying mode of action for its role as a radiosensitizer - while not entirely understood - is believed to arise from increased tumor blood flow, effects on cellular respiration, on cell signaling, and on the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS), that can act as radiosensitizers in their own right. NO activity is surprisingly long-lived and more potent in comparison to oxygen. Reports of the effects of NO with radiation have often been contradictory leading to confusion about the true radiosensitizing nature of NO. Whether increasing or decreasing tumor blood flow, acting as radiosensitizer or radioprotector, the effects of NO have been controversial. Key to understanding the role of NO as a radiosensitizer is to recognize the importance of biological context. With a very short half-life and potent activity, the local effects of NO need to be carefully considered and understood when using NO as a radiosensitizer. The systemic effects of NO donors can cause extensive side effects, and also affect the local tumor microenvironment, both directly and indirectly. To minimize systemic effects and maximize effects on tumors, agents that deliver NO on demand selectively to tumors using hypoxia as a trigger may be of greater interest as radiosensitizers. Herein we discuss the multiple effects of NO and focus on the clinical molecule RRx-001, a hypoxia-activated NO donor currently being investigated as a radiosensitizer in the clinic.
Keywords: Cancer; Hypoxia; Nitric oxide; Radiosensitization; Radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

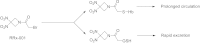
Similar articles
-
Rockets, radiosensitizers, and RRx-001: an origin story part I.Discov Med. 2016 Mar;21(115):173-80. Discov Med. 2016. PMID: 27115167 Review.
-
Nitric Oxide Donor-Based Cancer Therapy: Advances and Prospects.J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 28;60(18):7617-7635. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01672. Epub 2017 May 23. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28505442 Review.
-
RRx-001, A novel dinitroazetidine radiosensitizer.Invest New Drugs. 2016 Jun;34(3):371-7. doi: 10.1007/s10637-016-0326-y. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Invest New Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26841903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting tumor hypoxia with the epigenetic anticancer agent, RRx-001: a superagonist of nitric oxide generation.Med Oncol. 2016 Aug;33(8):85. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0798-9. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27377482
-
RRx-001, an epigenetic-based radio- and chemosensitizer, has vascular normalizing effects on SCCVII and U87 tumors.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 May 11;8:53. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0220-7. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27175220 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Improving the Efficacy of Common Cancer Treatments via Targeted Therapeutics towards the Tumour and Its Microenvironment.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 26;16(2):175. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020175. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Crosstalk between Malignant Plasma Cells and the Tumour Microenvironment in Multiple Myeloma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 24;14(11):2597. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112597. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NO control of mitochondrial function in normal and transformed cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2017 Aug;1858(8):573-581. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2017. PMID: 28216426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RRx-001 ameliorates inflammatory diseases by acting as a potent covalent NLRP3 inhibitor.Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Jun;18(6):1425-1436. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00683-y. Epub 2021 May 10. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33972740 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging targets for radioprotection and radiosensitization in radiotherapy.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11589-11609. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5117-8. Epub 2016 Jun 19. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27318945 Review.
References
-
- Sarti P., Avigliano L., Gorlach A., Brune B. Superoxide and nitric oxide – participation in cell communication. Cell Death Differ. 2002;9:1160–1162. - PubMed
-
- Feelisch M., Martin J.F. The early role of nitric oxide in evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995;10:496–499. - PubMed
-
- Yun H.Y., Dawson V.L., Dawson T.M. Nitric oxide in health and disease of the nervous system. Mol. Psychiatry. 1997;2:300–310. - PubMed
-
- Gladwin M.T., Schechter A.N. NO contest: nitrite versus S-nitroso-hemoglobin. Circ. Res. 2004;94:851–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

