Excessive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes midbrain floor plate neurogenesis, but results in vacillating dopamine progenitors
- PMID: 26164566
- PMCID: PMC4633300
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.07.002
Excessive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes midbrain floor plate neurogenesis, but results in vacillating dopamine progenitors
Abstract
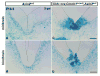
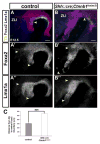
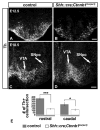
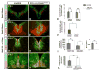
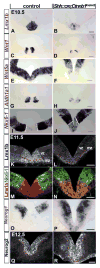
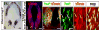
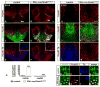
The floor plate (FP), a ventral midline structure of the developing neural tube, has differential neurogenic capabilities along the anterior-posterior axis. The midbrain FP, unlike the hindbrain and spinal cord floor plate, is highly neurogenic and produces midbrain dopaminergic (mDA) neurons. Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, at least in part, is thought to account for the difference in neurogenic capability. Removal of beta-catenin results in mDA progenitor specification defects as well as a profound reduction of neurogenesis. To examine the effects of excessive Wnt/beta-catenin signaling on mDA specification and neurogenesis, we have analyzed a model wherein beta-catenin is conditionally stabilized in the Shh+domain. Here, we show that the Foxa2+/Lmx1a+ domain is extended rostrally in mutant embryos, suggesting that canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling can drive FP expansion along the rostrocaudal axis. Although excess canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling generally promotes neurogenesis at midbrain levels, less tyrosine hydroxylase (Th)+, mDA neurons are generated, particularly impacting the Substantia Nigra pars compacta. This is likely because of improper progenitor specification. Excess canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling causes downregulation of net Lmx1b, Shh and Foxa2 levels in mDA progenitors. Moreover, these progenitors assume a mixed identity to that of Lmx1a+/Lmx1b+/Nkx6-1+/Neurog1+ progenitors. We also show by lineage tracing analysis that normally, Neurog1+ progenitors predominantly give rise to Pou4f1+ neurons, but not Th+ neurons. Accordingly, in the mutant embryos, Neurog1+ progenitors at the midline generate ectopic Pou4f1+ neurons at the expense of Th+ mDA neurons. Our study suggests that an optimal dose of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is critical for proper establishment of the mDA progenitor character. Our findings will impact embryonic stem cell protocols that utilize Wnt pathway reagents to derive mDA neuron models and therapeutics for Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Floor plate; Lmx1b; Midbrain dopaminergic neurons; Wnt/beta-catenin.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactions of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and sonic hedgehog regulate the neurogenesis of ventral midbrain dopamine neurons.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 7;30(27):9280-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0860-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20610763 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in midbrain dopaminergic neuron specification and neurogenesis.J Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;6(1):27-33. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjt043. Epub 2013 Nov 28. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24287202 Review.
-
Ectopic Wnt/beta-catenin signaling induces neurogenesis in the spinal cord and hindbrain floor plate.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030266. Epub 2012 Jan 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22276170 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt antagonism of Shh facilitates midbrain floor plate neurogenesis.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Feb;12(2):125-31. doi: 10.1038/nn.2243. Epub 2009 Jan 4. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19122665
-
Foxa1 and Foxa2 transcription factors regulate differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;651:58-65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0322-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19731550 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose-Dependent and Subset-Specific Regulation of Midbrain Dopaminergic Neuron Differentiation by LEF1-Mediated WNT1/b-Catenin Signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 26;8:587778. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.587778. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195246 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition of the Midbrain Dopaminergic Neuronal Identity.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4638. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134638. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32629812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Approaches and Molecular Mechanisms for Directly Reprogramming Fibroblasts Into Neurons and Dopamine Neurons.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Sep 29;13:738529. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.738529. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34658841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel floor plate boundary defined by adjacent En1 and Dbx1 microdomains distinguishes midbrain dopamine and hypothalamic neurons.Development. 2017 Mar 1;144(5):916-927. doi: 10.1242/dev.144949. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Development. 2017. PMID: 28174244 Free PMC article.
-
Pluripotent stem cell derived dopaminergic subpopulations model the selective neuron degeneration in Parkinson's disease.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Nov 9;16(11):2718-2735. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.09.014. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 34678205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderegg A, Lin HP, Chen JA, Caronia-Brown G, Cherepanova N, Yun B, Joksimovic M, Rock J, Harfe BD, Johnson R, Awatramani R. An Lmx1b-miR135a2 regulatory circuit modulates Wnt1/Wnt signaling and determines the size of the midbrain dopaminergic progenitor pool. PLoS genetics. 2013;9:e1003973. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersson E, Tryggvason U, Deng Q, Friling S, Alekseenko Z, Robert B, Perlmann T, Ericson J. Identification of intrinsic determinants of midbrain dopamine neurons. Cell. 2006;124:393–405. - PubMed
-
- Blaess S, Bodea GO, Kabanova A, Chanet S, Mugniery E, Derouiche A, Stephen D, Joyner AL. Temporal-spatial changes in Sonic Hedgehog expression and signaling reveal different potentials of ventral mesencephalic progenitors to populate distinct ventral midbrain nuclei. Neural Dev. 2011;6:29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blaess S, Corrales JD, Joyner AL. Sonic hedgehog regulates Gli activator and repressor functions with spatial and temporal precision in the mid/hindbrain region. Development. 2006;133:1799–1809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

