Determinants of hepatitis B and delta virus host tropism
- PMID: 26164658
- PMCID: PMC4550528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.06.004
Determinants of hepatitis B and delta virus host tropism
Abstract
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are a global health problem afflicting approximately 360 million patients. Of these individuals, 15-20 million are co-infected with hepatitis delta virus (HDV). Progress toward curative therapies has been impeded by the highly restricted host tropism of HBV, which is limited to productive infections in humans and chimpanzees. Here, we will discuss different approaches that have been taken to study HBV and HDV infections in vivo. The development of transgenic and humanized mice has lead to deeper insights into HBV pathogenesis. An improved understanding of the determinants governing HBV and HDV species tropism will aid in the construction of a small animal model with inheritable susceptible to HBV/HDV.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


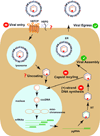
References
-
- Hughes SA, Wedemeyer H, Harrison PM. Hepatitis delta virus. Lancet. 2011;378:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Dienstag JL. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1486–1500. - PubMed
-
-
Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, Purcell RH, Chisari FV. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol. 2003;77:68–76. Showcased the importance of the T cell response in viral clearence for HBV acute infections.
-
-
- Rizzetto M, Canese MG, Gerin JL, London WT, Sly DL, Purcell RH. Transmission of the hepatitis B virus-associated delta antigen to chimpanzees. J. Infect. Dis. 1980;141:590–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

