Novel Biomarkers of Cardiac Stress, Cardiovascular Dysfunction, and Outcomes in HIV-Infected Individuals
- PMID: 26164679
- PMCID: PMC4529774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchf.2015.03.007
Novel Biomarkers of Cardiac Stress, Cardiovascular Dysfunction, and Outcomes in HIV-Infected Individuals
Abstract
Objectives: This study sought to determine whether biomarkers ST2, growth differentiation factor (GDF)-15, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and high-sensitivity troponin I are elevated in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and are associated with cardiovascular dysfunction and all-cause mortality.
Background: HIV-infected patients have high rates of cardiovascular disease. Markers of myocardial stress may identify at-risk patients and provide additional prognostic information.
Methods: Biomarkers and echocardiograms were assessed in 332 HIV-infected patients and 50 age- and sex-matched control subjects. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction was defined as ejection fraction <50%, diastolic dysfunction (DD) as stage 1 or higher, and pulmonary hypertension as pulmonary artery systolic pressure ≥35 mm Hg. Mortality data were obtained from the National Death Index.
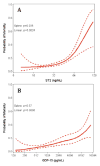
Results: Patients with HIV had a median age of 49 years, and 80% were male. Compared with control subjects, HIV-infected patients had higher adjusted percent estimates of all biomarkers except ST2 and interleukin-6. Among HIV-infected patients, 45% had DD; only ST2 was associated with DD (relative risk [RR]: 1.36; p = 0.047). Left ventricular systolic dysfunction was rare in this cohort (5%). Pulmonary hypertension was present in 27% of HIV-infected patients and was associated with GDF-15 (RR: 1.18; p = 0.04), NT-proBNP (RR: 1.18; p = 0.007), and cystatin C (RR: 1.54; p = 0.03). Thirty-eight deaths occurred among HIV-infected patients over a median of 6.1 years. In adjusted analysis, all-cause mortality was independently predicted by ST2 (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.04; p = 0.010), GDF-15 (HR: 1.42; p = 0.0054), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (HR: 1.25; p = 0.023), and D-dimer (HR: 1.49; p = 0.029). Relationships were unchanged when analyses were restricted to virally suppressed HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy.
Conclusions: Among HIV-infected patients, ST2 and GDF-15 were associated with both cardiovascular dysfunction and all-cause mortality, and these variables may be useful at identifying those at risk for developing cardiovascular events and death.
Keywords: HIV; biomarkers; cardiovascular dysfunction; death; mortality.
Copyright © 2015 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Broad Spectrum of HIV-Related Cardiovascular Disease.JACC Heart Fail. 2015 Aug;3(8):600-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2015.04.007. Epub 2015 Jul 8. JACC Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 26164680 No abstract available.
References
-
- Stein JH, Hsue PY. Inflammation, immune activation, and CVD risk in individuals with HIV infection. JAMA. 2012;308:405–6. - PubMed
-
- Boccara F, Lang S, Meuleman C, et al. HIV and coronary heart disease: time for a better understanding. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:511–23. - PubMed
-
- El-Sadr WM, Lundgren JD, Neaton JD, et al. CD4+ count-guided interruption of antiretroviral treatment. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2283–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

