Postnatal neurodevelopmental expression and glutamate-dependent regulation of the ZNF804A rodent homologue
- PMID: 26164821
- PMCID: PMC4591171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2015.06.023
Postnatal neurodevelopmental expression and glutamate-dependent regulation of the ZNF804A rodent homologue
Abstract
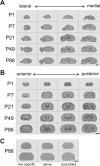
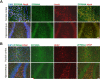
The zinc finger protein ZNF804A rs1344706 variant is a replicated genome-wide significant risk variant for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. While its association with altered brain structure and cognition in patients and healthy risk allele carriers is well documented, the characteristics and function of the gene in the brain remains poorly understood. Here, we used in situ hybridization to determine mRNA expression levels of the ZNF804A rodent homologue, Zfp804a, across multiple postnatal neurodevelopmental time points in the rat brain. We found changes in Zfp804a expression in the rat hippocampus, frontal cortex, and thalamus across postnatal neurodevelopment. Zfp804a mRNA peaked at postnatal day (P) 21 in hippocampal CA1 and DG regions and was highest in the lower cortical layers of frontal cortex at P1, possibly highlighting a role in developmental migration. Using immunofluorescence, we found that Zfp804a mRNA and ZFP804A co-localized with neurons and not astrocytes. In primary cultured cortical neurons, we found that Zfp804a expression was significantly increased when neurons were exposed to glutamate [20μM], but this increase was blocked by the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist MK-801. Expression of Comt, Pde4b, and Drd2, genes previously shown to be regulated by ZNF804A overexpression, was also significantly changed in an NMDA-dependent manner. Our results describe, for the first time, the unique postnatal neurodevelopmental expression of Zfp804a in the rodent brain and demonstrate that glutamate potentially plays an important role in the regulation of this psychiatric susceptibility gene. These are critical steps toward understanding the biological function of ZNF804A in the mammalian brain.
Keywords: Gene expression; In situ hybridization; Neurodevelopment; Schizophrenia; ZNF804A; Zfp804a.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interactome analysis reveals ZNF804A, a schizophrenia risk gene, as a novel component of protein translational machinery critical for embryonic neurodevelopment.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;23(4):952-962. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.166. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28924186 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia-Like Deficits and Impaired Glutamate/Gamma-aminobutyric acid Homeostasis in Zfp804a Conditional Knockout Mice.Schizophr Bull. 2024 Nov 8;50(6):1411-1426. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbae120. Schizophr Bull. 2024. PMID: 38988003 Free PMC article.
-
The Rat Homolog of the Schizophrenia Susceptibility Gene ZNF804A Is Highly Expressed during Brain Development, Particularly in Growth Cones.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132456. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26148198 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic analyses and conceptual synthesis of evidence linking ZNF804A to risk for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015 Jan;168B(1):14-35. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32284. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25522715 Review.
-
Regulation of the NMDA receptor: implications for neuropsychological development.Nutr Rev. 2006 Sep;64(9):428-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00228.x. Nutr Rev. 2006. PMID: 17002239 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc in Cognitive Impairment and Aging.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 18;12(7):1000. doi: 10.3390/biom12071000. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The schizophrenia risk gene ZNF804A: clinical associations, biological mechanisms and neuronal functions.Mol Psychiatry. 2017 Jul;22(7):944-953. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.19. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28289284 Review.
-
Interactome analysis reveals ZNF804A, a schizophrenia risk gene, as a novel component of protein translational machinery critical for embryonic neurodevelopment.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Apr;23(4):952-962. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.166. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28924186 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia-Like Deficits and Impaired Glutamate/Gamma-aminobutyric acid Homeostasis in Zfp804a Conditional Knockout Mice.Schizophr Bull. 2024 Nov 8;50(6):1411-1426. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbae120. Schizophr Bull. 2024. PMID: 38988003 Free PMC article.
-
A promoter variant in ZNF804A decreasing its expression increases the risk of autism spectrum disorder in the Han Chinese population.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Jan 22;9(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0369-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30670685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benes FM, McSparren J, Bird ED, SanGiovanni JP, Vincent SL. Deficits in small interneurons in prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulated cortices of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 1991;48:996–1001. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Xu Z, Zhai J, Bao X, Zhang Q, Gu H, Shen Q, Cheng L, Chen X, Wang K, Deng X, Ji F, Liu C, Li J, Dong Q, Chen C. Evidence of IQ-modulated association between ZNF804A gene polymorphism and cognitive function in schizophrenia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(7):1572–1578. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

