A preliminary study of the effect of ECRG4 overexpression on the proliferation and apoptosis of human laryngeal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms
- PMID: 26165988
- PMCID: PMC4581775
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4059
A preliminary study of the effect of ECRG4 overexpression on the proliferation and apoptosis of human laryngeal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms
Abstract
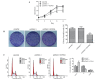
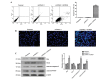
Human esophageal cancer‑related gene 4 (ECRG4) is a potential tumor suppressor gene isolated from human esophageal epithelial cells. Studies have shown that ECRG4 effectively inhibits the proliferation of tumor cells and induces apoptosis. However, the role of ECRG4 in laryngeal cancer has not yet been clearly defined. In this study, a human laryngeal cancer cell line stably overexpressing ECRG4 was established. The effect of ECRG4 on the proliferation and apoptosis of laryngeal cancer cells and the associated mechanisms were investigated. The Hep‑2 human laryngeal carcinoma cell line exhibited a low basal level of ECRG4 expression and was selected for the present study. The eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA3.1‑ECRG4 was constructed and introduced into Hep‑2 cells by transfection reagents. Western blot analysis, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence staining confirmed high‑level expression of ECRG4. The 3‑(4, 5‑dimethylthiazol‑2‑yl)‑2,5‑diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay and colony formation assay showed that ECRG4 overexpression suppressed the proliferative capacity of laryngeal cancer cells in vitro. Cell cycle analysis showed that ECRG4 induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase. Flow cytometric analysis and Hoechst staining demonstrated that overexpression of ECRG4 significantly induced apoptosis. Western blot analysis confirmed that Bcl‑2‑associated X protein, cleaved‑caspase‑3 and cleaved‑poly (ADP‑ribose) polymerase were upregulated in the apoptotic process, whereas B‑cell lymphoma 2 was downregulated. In conclusion, overexpression of ECRG4 inhibited laryngeal cancer cell proliferation and induced cancer cell apoptosis. Therefore, ECRG4 exhibits potential as an effective target in gene therapy for laryngeal cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ECRG4 acts as a tumor suppressor gene frequently hypermethylated in human breast cancer.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 10;39(5):BSR20190087. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190087. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30918105 Free PMC article.
-
ECRG4: a new potential target in precision medicine.Front Med. 2019 Oct;13(5):540-546. doi: 10.1007/s11684-018-0637-9. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Front Med. 2019. PMID: 30003403 Review.
-
Costunolide Induces Apoptosis through Generation of ROS and Activation of P53 in Human Esophageal Cancer Eca-109 Cells.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016 Sep;30(9):462-9. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21810. Epub 2016 Apr 14. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27078502
-
Purine analogue ENERGI-F706 induces apoptosis of 786-O renal carcinoma cells via 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):4566-4571. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3906. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26062651
-
Potential functions of esophageal cancer-related gene-4 in the cardiovascular system.Front Med. 2019 Dec;13(6):639-645. doi: 10.1007/s11684-019-0701-0. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Front Med. 2019. PMID: 31468282 Review.
Cited by
-
ECRG4 acts as a tumor suppressor gene frequently hypermethylated in human breast cancer.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 10;39(5):BSR20190087. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190087. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30918105 Free PMC article.
-
Complex and pleiotropic signaling pathways regulated by the secreted protein augurin.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Apr 11;21(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01090-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37041625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 Attenuates Triptolide-Induced Cytotoxicity in HL-7702 Cells via the Activation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:723784. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.723784. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046796 Free PMC article.
-
ECRG4: a new potential target in precision medicine.Front Med. 2019 Oct;13(5):540-546. doi: 10.1007/s11684-018-0637-9. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Front Med. 2019. PMID: 30003403 Review.
-
Downregulation and DNA methylation of ECRG4 in gastric cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Jul 13;11:4019-4028. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S161200. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30034241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaseviciene L, Gurevicius R, Obelenis V, Cicenas S, Juozulynas A. Trends in laryngeal cancer incidence in Lithuania: A future perspective. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2004;17:473–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

