Hepatic encephalopathy coexists with acquired chronic hepatocerebral degeneration
- PMID: 26166598
- PMCID: PMC4710335
- DOI: 10.17712/nsj.2015.3.20140759
Hepatic encephalopathy coexists with acquired chronic hepatocerebral degeneration
Abstract
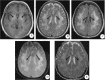
Hyperkinetic extrapyramidal syndrome is the typical clinical characteristic of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration (AHD), but is usually not observed with hepatic encephalopathy (HE). We present a case of AHD coexisting with HE. Both conditions were secondary to liver cirrhosis and hepatitis C virus infection. The brain MRI showed bilateral and symmetric high T1 signal-intensity in the globus pallidus, and diffuse high signal-intensity of the hemispheric white matter on T2-FLAIR images. As we usually neglect the existence of AHD, the diagnosis is often ignored, especially when it coexists with HE. This case highlights the need to distinguish irreversible AHD from HE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration and hepatic encephalopathy: correlations and variety of clinical presentations in overt and subclinical liver disease.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2011 Jun;69(3):496-501. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x2011000400017. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2011. PMID: 21755129
-
Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: MR similarity with Wilson disease.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988 Nov-Dec;12(6):1076-7. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988. PMID: 3183119
-
Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: clinical characteristics and MRI findings.Eur J Neurol. 2010 Dec;17(12):1463-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03076.x. Eur J Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20491897
-
Recent Updates on Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration.Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2017 Sep 5;7:463. doi: 10.7916/D8TB1K44. eCollection 2017. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2017. PMID: 28975044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: a case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Feb 7;11(5):764-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.764. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15655841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating Diagnostic Challenges: A Case of Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration Presenting as Worsening Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Disease.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024 Jun 28;11(7):004629. doi: 10.12890/2024_004629. eCollection 2024. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38984190 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese, a Likely Cause of 'Parkinson's in Cirrhosis', a Unique Clinical Entity of Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration.Cureus. 2020 Sep 14;12(9):e10448. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10448. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33072457 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sturgeon JP, Shawcross DL. Recent insights into the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and treatments. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;8:83–100. - PubMed
-
- Dhiman RK, Kurmi R, Thumburu KK, Venkataramarao SH, Agarwal R, Duseja A, et al. Diagnosis and prognostic significance of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis of liver. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:2381–2390. - PubMed
-
- Maffeo E, Montuschi A, Stura G, Giordana MT. Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration, pallidal T1 MRI hyperintensity and manganese in a series of cirrhotic patients. Neurol Sci. 2014;35:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Stracciari A, Baldin E, Cretella L, Delaj L, D’Alessandro R, Guarino M. Chronic acquired hepatocerebral degeneration: effects of liver transplantation on neurological manifestations. Neurol Sci. 2011;32:411–415. - PubMed
-
- Ishihara T, Ito M, Watanabe H, Ishigami M, Kiuchi T, Sobue G. [Case of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration with prominent improvement of parkinsonism and cognitive deficits after living-donor liver transplantation] Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2012;52:581–584. Japanese. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
