Synthesis, structure, and antimicrobial activity of heterocyclic phenylsulfonyl- and 4-aminophenylsulfonyl-carboximidamides
- PMID: 26166869
- PMCID: PMC4494770
- DOI: 10.1007/s00706-012-0769-6
Synthesis, structure, and antimicrobial activity of heterocyclic phenylsulfonyl- and 4-aminophenylsulfonyl-carboximidamides
Abstract
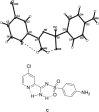
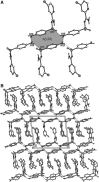
Abstract: A series of novel phenylsulfonyl- and 4-aminophenylsulfonyl-carboximidamides were synthesized by condensation of sulfonamides with heterocyclic methyl carbimidates obtained from heterocyclic carbonitriles and used 'at its inception.' The molecular structure of the obtained compounds is discussed. Compounds possessing heterocyclic systems with a nitrogen atom in the α position to the functional group showed a different single-crystal structure than expected. The synthesized derivatives were evaluated for antimicrobial activities: tuberculostatic, antibacterial, and antifungal.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity; Crystal structure; Heterocycles; Structure–activity relationship; Sulfonamidine; Synthesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis, structure, and biological activity of novel heterocyclic sulfonyl-carboximidamides.Monatsh Chem. 2013;144(5):647-658. doi: 10.1007/s00706-012-0888-0. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Monatsh Chem. 2013. PMID: 26166881 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological activity of novel 3-heteroaryl-2H-pyrido[4,3-e][1,2,4]thiadiazine and 3-heteroaryl-2H-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-dioxides.Monatsh Chem. 2013;144(8):1197-1203. doi: 10.1007/s00706-013-0988-5. Epub 2013 May 14. Monatsh Chem. 2013. PMID: 26166884 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of novel heterocyclic sulfamoyl-phenyl-carboximidamides derived from clinically applied sulfonamides.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2012 Nov;345(11):911-7. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201200160. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2012. PMID: 22886614
-
Quinazolinone and quinazoline derivatives: recent structures with potent antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities.Res Pharm Sci. 2016 Jan-Feb;11(1):1-14. Res Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27051427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tandem construction of biological relevant aliphatic 5-membered N-heterocycles.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 May 5;235:114303. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114303. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35344904 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, structure, and biological activity of novel heterocyclic sulfonyl-carboximidamides.Monatsh Chem. 2013;144(5):647-658. doi: 10.1007/s00706-012-0888-0. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Monatsh Chem. 2013. PMID: 26166881 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological activity of novel 3-heteroaryl-2H-pyrido[4,3-e][1,2,4]thiadiazine and 3-heteroaryl-2H-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-dioxides.Monatsh Chem. 2013;144(8):1197-1203. doi: 10.1007/s00706-013-0988-5. Epub 2013 May 14. Monatsh Chem. 2013. PMID: 26166884 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of New N-acyl Hydrazone Derivatives of Carprofen as Potential Tuberculostatic Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;13(3):212. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030212. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534647 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, anticancer and antibacterial activity of salinomycin N-benzyl amides.Molecules. 2014 Nov 25;19(12):19435-59. doi: 10.3390/molecules191219435. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25429565 Free PMC article.
-
Access to amidines via C(sp2)-N coupling of trifluoroborate-iminiums with N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide.Chem Sci. 2025 Jun 3;16(26):12012-12023. doi: 10.1039/d5sc02912k. eCollection 2025 Jul 2. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40469763 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
