Predictive factors for lymph node positivity in patients undergoing extended pelvic lymphadenectomy during robot assisted radical prostatectomy
- PMID: 26166965
- PMCID: PMC4495496
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.156918
Predictive factors for lymph node positivity in patients undergoing extended pelvic lymphadenectomy during robot assisted radical prostatectomy
Abstract
Introduction: Pelvic lymphadenectomy during radical prostatectomy (RP) improves staging and may provide a therapeutic benefit. However, there is no clear consensus on the selection criteria for subjecting patients to this additional procedure. With a growing adoption of robot assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) in India, it has become imperative to study the incidence and predictive factors for lymph node involvement in our patients.
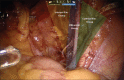
Materials and methods: From February 2010 to February 2014, 452 RARP procedures were performed at our institution. A total of 100 consecutive patients from July 2011 to August 2012 were additionally subjected to a robotic extended pelvic lymphadenectomy (EPLND). Lymph node positivity rates and lymph node density were analyzed on the basis of preoperative prostate specific antigen (PSA), Gleason score, clinical stage, D'Amico risk category and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. Multivariate analysis was performed to ascertain factors associated with lymph node positivity in our cohort.
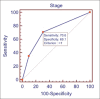
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.5 (47-77) years and the body mass index was 26.3 (16.3-38.7) kg/m(2). The mean console time for EPLND was 45 (32-68) min. A median of 17 (two to 40) lymph nodes were retrieved. Seventeen patients (17%) had positive lymph nodes (median of 1, range 1-6). Median lymph node density in these patients was 10%. When stratified by PSA, Gleason score, clinical stage, D'Amico risk category and features of locally advanced disease on MRI, a trend towards increasing incidence of lymph node positivity was observed, with an increase in adverse factors. However, on multivariate analysis, clinical stage > T2a was the only significant factor impacting lymph node positivity in our cohort.
Conclusions: A significant proportion of men undergoing RARP in India have positive lymph nodes on EPLND. While other variables may also have a potential impact, a higher clinical stage predisposes to an increased incidence of lymph node metastases.
Keywords: Extended pelvic lymphadenectomy; pelvic lymphadenectomy; prostate cancer; radical prostatectomy; robot assisted radical prostatectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extended pelvic lymphadenectomy in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy: high incidence of lymph node metastasis.J Urol. 2002 Apr;167(4):1681-6. J Urol. 2002. PMID: 11912387
-
Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy and Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection in Patients with Locally-advanced Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol. 2017 Feb;71(2):249-256. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 May 18. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27209538
-
Extended versus standard pelvic lymphadenectomy during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: the role of extended template as an independent predictor of lymph node invasion with comparable morbidity burden.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2017 Oct;69(5):475-485. doi: 10.23736/S0393-2249.17.02838-7. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2017. PMID: 28281741
-
[Significance and Importance of Pelvic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients].Aktuelle Urol. 2016 Sep;47(5):402-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-104788. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Aktuelle Urol. 2016. PMID: 27680192 Review. German.
-
Anatomical extent of pelvic lymphadenectomy in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy.Eur Urol. 2007 Jul;52(1):29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.04.020. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Eur Urol. 2007. PMID: 17448592 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparison between 68Ga-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen-PET/CT and multiparametric MRI for excluding regional metastases prior to radical prostatectomy.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020 Dec;45(12):4194-4201. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02640-1. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020. PMID: 32671440
-
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging-transrectal ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy: A prospective, single centre study.Indian J Urol. 2017 Apr-Jun;33(2):134-139. doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.203414. Indian J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28469301 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of nomograms for predicting pentafecta outcomes before and after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):2079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86120-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39814834 Free PMC article.
-
MRI and 11C Acetate PET/CT for Prediction of Regional Lymph Node Metastasis in Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer.Radiol Oncol. 2018 Jan 24;52(1):90-97. doi: 10.2478/raon-2018-0001. eCollection 2018 Mar. Radiol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29520210 Free PMC article.
-
External Validation of Briganti and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Centre Nomograms for Predicting Lymph Node Invasion in the Indian Cohort of Patients with Prostate Cancer.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025 Apr;16(2):450-455. doi: 10.1007/s13193-023-01732-w. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40337042
References
-
- Montorsi F, Wilson TG, Rosen RC, Ahlering TE, Artibani TE, Carroll PR, et al. Best practices in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Recommendations of the Pasadena Consensus Panel. Eur Urol. 2012;62:368–81. - PubMed
-
- Novara G, Ficarra V, Rosen RC, Artibani W, Costello A, Eastham JA, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes and complications after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:431–52. - PubMed
-
- Ficarra V, Novara G, Rosen RC, Artibani W, Carroll PR, Costello A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:405–17. - PubMed
-
- Novara G, Ficarra V, Mocellin S, Ahlering TE, Carroll PR, Graefen M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting oncologic outcome after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:382–404. - PubMed
-
- Ficarra V, Novara G, Ahlering TE, Costello A, Eastham JA, Graefen M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting potency rates after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:418–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

