Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of new N-phenyl-2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)acetamide derivatives
- PMID: 26167103
- PMCID: PMC4491109
- DOI: 10.1007/s00044-015-1360-6
Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of new N-phenyl-2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)acetamide derivatives
Abstract
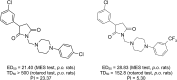
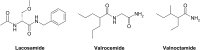
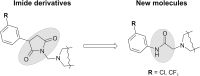
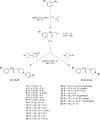
Twenty-two new N-phenyl-2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)acetamide derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for their anticonvulsant activity in animal models of epilepsy. These molecules have been designed as analogs of previously obtained anticonvulsant active pyrrolidine-2,5-diones in which heterocyclic imide ring has been changed into chain amide bound. The final compounds were synthesized in the alkylation reaction of the corresponding amines with the previously obtained alkylating reagents 2-chloro-1-(3-chlorophenyl)ethanone (1) or 2-chloro-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanone (2). Initial anticonvulsant screening was performed using standard maximal electroshock (MES) and subcutaneous pentylenetetrazole screens in mice and/or rats. Several compounds were tested additionally in the psychomotor seizures (6-Hz model). The acute neurological toxicity was determined applying the rotarod test. The results of pharmacological studies showed activity exclusively in the MES seizures especially for 3-(trifluoromethyl)anilide derivatives, whereas majority of 3-chloroanilide analogs were inactive. It should be emphasize that several molecules showed also activity in the 6-Hz screen which is an animal model of human partial and therapy-resistant epilepsy. In the in vitro studies, the most potent derivative 20 was observed as moderate binder to the neuronal voltage-sensitive sodium channels (site 2). The SAR studies for anticonvulsant activity confirmed the crucial role of pyrrolidine-2,5-dione core fragment for anticonvulsant activity.
Keywords: Anticonvulsant activity; Epilepsy; In vitro studies; In vivo studies; Phenylacetamides; SAR studies.
Figures
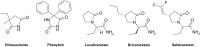
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of new 1-[2-oxo-2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl]pyrrolidine-2,5-diones.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Oct 1;21(19):5800-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.07.118. Epub 2011 Aug 6. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21875804
-
Synthesis, anticonvulsant properties, and SAR analysis of differently substituted pyrrolidine-2,5-diones and piperidine-2,6-diones.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014 Nov;347(11):840-52. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201400179. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014. PMID: 25196991
-
New hybrid molecules with anticonvulsant and antinociceptive activity derived from 3-methyl- or 3,3-dimethyl-1-[1-oxo-1-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)propan-2-yl]pyrrolidine-2,5-diones.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Feb 15;24(4):606-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.12.027. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26746343
-
Design, synthesis and anticonvulsant properties of new N-Mannich bases derived from 3-phenylpyrrolidine-2,5-diones.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Nov 1;21(21):6821-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.07.029. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23993970
-
Synthesis and biological properties of new N-Mannich bases derived from 3-methyl-3-phenyl- and 3,3-dimethyl-succinimides. Part V.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Aug;66:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 May 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23777899
Cited by
-
BSA/DNA binding behavior and the photophysicochemical properties of novel water soluble zinc(II)phthalocyanines directly substituted with piperazine groups.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021 Jun;26(4):455-465. doi: 10.1007/s00775-021-01868-6. Epub 2021 May 4. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33944997
-
Fundamental origins of neural tube defects with a basis in genetics and nutrition.Exp Brain Res. 2025 Mar 2;243(4):79. doi: 10.1007/s00221-025-07016-9. Exp Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40025180 Review.
-
Development and pharmacologic characterization of the rat 6 Hz model of partial seizures.Epilepsia. 2017 Jun;58(6):1073-1084. doi: 10.1111/epi.13764. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28449218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell GS, Sander JW. The epidemiology of epilepsy: the size of the problem. Seizure. 2002;11(Suppl A):306–314. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
