Erythropoietin and obesity-induced white adipose tissue inflammation: redefining the boundaries of the immunometabolism territory
- PMID: 26167420
- PMCID: PMC4496980
- DOI: 10.4161/21623945.2014.978654
Erythropoietin and obesity-induced white adipose tissue inflammation: redefining the boundaries of the immunometabolism territory
Abstract
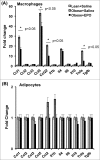
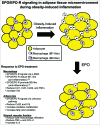
The adipose tissue represents a critical and predominant site for the interaction between metabolic and inflammatory responses during health and disease. In the white adipose tissue microenvironment, macrophages/adipocytes cross-talk have been shown to influence the metabolic and inflammatory states of both cell types, and contribute to the development of systemic insulin resistance during obesity. Indeed, the existence of paracrine loops between mature adipocytes and macrophages, especially during obesity-induced stress, involving the release of, and response to, an array of cytokines and regulatory factors, have been extensively studied using several in vitro and in vivo model systems. Published evidence together with recent observations, brought to light the unexpected role of erythropoietin and its receptor in the regulation of white adipose tissue mass, energy homeostasis, and inflammation as demonstrated by erythropoietin effects on adipocyte development and metabolic profile, and macrophage infiltration, cytokine responses, and activation state during diet-induced obesity. In this commentary, we discuss the newly added elements and perspectives to our understanding of the erythropoietin/erythropoietin-receptor axis as a regulator of obesity-induced white adipose tissue inflammation, providing insight into its effects on cytokine responses of macrophages and adipocytes, and possible links to glucose metabolism and insulin resistance.
Keywords: adipocytes; chemokines; cytokines; erythropoietin; erythropoietin receptor; immunometabolism; macrophages; obesity-induced inflammation; white adipose tissue.
Figures
References
-
- Zeyda M, Stulnig T: Obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance-a mini-review. Gerontology 2009; 55: 379-86; PMID:19365105; http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000212758 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olefsky JM, Glass CK: Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 2010; 72:219-46; PMID:20148674; http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR: Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 2011; 121(6): 2111-7; PMID:21633179; http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI57132 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han JM. and Levings MK. Immune regulation in obesity-associated adipose inflammation. J Immunol 2013; 191(2):527-32; PMID:23825387; http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1301035 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schneider A, Schneider MP, Scharnagl H, Jardine AG, Wanner C, Drechsler C. Predicting erythropoietin resistance in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Nephrol 2013; 14: 67; PMID:23521816; http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-14-67 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
