Changes in urinary excretion of water and sodium transporters during amiloride and bendroflumethiazide treatment
- PMID: 26167467
- PMCID: PMC4491934
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i3.423
Changes in urinary excretion of water and sodium transporters during amiloride and bendroflumethiazide treatment
Abstract
Aim: To quantify changes in urinary excretion of aquaporin2 water channels (u-AQP2), the sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter (u-NKCC2) and the epithelial sodium channels (u-ENaC) during treatment with bendroflumethiazide (BFTZ), amiloride and placebo.
Methods: In a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, 3-way crossover study we examined 23 healthy subjects on a standardized diet and fluid intake. The subjects were treated with amiloride 5 mg, BFTZ 1.25 mg or placebo twice a day for 4.5 d before each examination day. On the examination day, glomerular filtration rate was measured by the constant infusion clearance technique with (51)Cr-EDTA as reference substance. To estimate the changes in water transport via AQP2 and sodium transport via NKCC2 and ENaC, u-NKCC2, the gamma fraction of ENaC (u-ENaCγ), and u-AQP2 were measured at baseline and after infusion with 3% hypertonic saline. U-NKCC2, u-ENaCγ, u-AQP2 and plasma concentrations of vasopressin (p-AVP), renin (PRC), angiotensin II (p-ANG II) and aldosterone (p-Aldo) were measured, by radioimmunoassay. Central blood pressure was estimated by applanation tonometry and body fluid volumes were estimated by bio-impedance spectroscopy. General linear model with repeated measures or related samples Friedman's two-way analysis was used to compare differences. Post hoc Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons of post infusion periods to baseline within each treatment group.
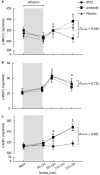
Results: At baseline there were no differences in u-NKCC2, u-ENaCγ and u-AQP2. PRC, p-Ang II and p-Aldo were increased during active treatments (P < 0.001). After hypertonic saline, u-NKCC2 increased during amiloride (6% ± 34%; P = 0.081) and increased significantly during placebo (17% ± 24%; P = 0.010). U-AQP2 increased significantly during amiloride (31% ± 22%; P < 0.001) and placebo (34% ± 27%; P < 0.001), while u-NKCC2 and u-AQP2 did not change significantly during BFTZ (-7% ± 28%; P = 0.257 and 5% ± 16%; P = 0.261). U- ENaCγ increased in all three groups (P < 0.050). PRC, AngII and p-Aldo decreased to the same extent, while AVP increased, but to a smaller degree during BFTZ (P = 0.048). cDBP decreased significantly during BFTZ (P < 0.001), but not during amiloride or placebo. There were no significant differences in body fluid volumes.
Conclusion: After hypertonic saline, u-NKCC2 and u-AQP2 increased during amiloride, but not during BFTZ. Lower p-AVP during BFTZ potentially caused less stimulation of NKCC2 and AQP2 and subsequent lower reabsorption of water and sodium.
Keywords: Amiloride; Aquaporin2; Epithelial sodium channels; Hypertonic saline; Sodium; Sodium transporters; Sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter; Thiazide; Urine; Water.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of volume expansion with hypertonic- and isotonic saline and isotonic glucose on sodium and water transport in the principal cells in the kidney.BMC Nephrol. 2013 Sep 26;14:202. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-202. BMC Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 24067081 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of amiloride and spironolactone on renal tubular function and central blood pressure in patients with arterial hypertension during baseline conditions and after furosemide: a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover trial.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2013;35(5):313-24. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2012.721843. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 22966789 Clinical Trial.
-
Abnormal urinary excretion of NKCC2 and AQP2 in response to hypertonic saline in chronic kidney disease: an intervention study in patients with chronic kidney disease and healthy controls.BMC Nephrol. 2014 Jun 26;15:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-101. BMC Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24970686 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Abnormal increase in urinary aquaporin-2 excretion in response to hypertonic saline in essential hypertension.BMC Nephrol. 2012 Mar 27;13:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-15. BMC Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22452789 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 after furosemide and felodipine in healthy humans.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2005;65(3):249-61. doi: 10.1080/00365510510013659. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2005. PMID: 16095054 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Breviscapine prevents downregulation of renal water and sodium transport proteins in response to unilateral ureteral obstruction.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 May;19(5):573-8. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2016.6943. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27403265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleyman TR, Cragoe EJ. Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988;105:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen S, Agre P. The aquaporin family of water channels in kidney. Kidney Int. 1995;48:1057–1068. - PubMed
-
- Kanno K, Sasaki S, Hirata Y, Ishikawa S, Fushimi K, Nakanishi S, Bichet DG, Marumo F. Urinary excretion of aquaporin-2 in patients with diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1540–1545. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

