An siRNA-based functional genomics screen for the identification of regulators of ciliogenesis and ciliopathy genes
- PMID: 26167768
- PMCID: PMC4536769
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3201
An siRNA-based functional genomics screen for the identification of regulators of ciliogenesis and ciliopathy genes
Abstract
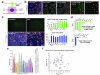
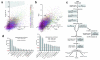
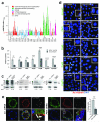
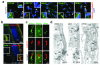
Defects in primary cilium biogenesis underlie the ciliopathies, a growing group of genetic disorders. We describe a whole-genome siRNA-based reverse genetics screen for defects in biogenesis and/or maintenance of the primary cilium, obtaining a global resource. We identify 112 candidate ciliogenesis and ciliopathy genes, including 44 components of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, 12 G-protein-coupled receptors, and 3 pre-mRNA processing factors (PRPF6, PRPF8 and PRPF31) mutated in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. The PRPFs localize to the connecting cilium, and PRPF8- and PRPF31-mutated cells have ciliary defects. Combining the screen with exome sequencing data identified recessive mutations in PIBF1, also known as CEP90, and C21orf2, also known as LRRC76, as causes of the ciliopathies Joubert and Jeune syndromes. Biochemical approaches place C21orf2 within key ciliopathy-associated protein modules, offering an explanation for the skeletal and retinal involvement observed in individuals with C21orf2 variants. Our global, unbiased approaches provide insights into ciliogenesis complexity and identify roles for unanticipated pathways in human genetic disease.
Figures



References
-
- Adams M, Smith UM, Logan CV, Johnson CA. Recent advances in the molecular pathology, cell biology and genetics of ciliopathies. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2008;45:257–267. - PubMed
-
- Quinlan RJ, Tobin JL, Beales PL. Modeling ciliopathies: Primary cilia in development and disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;84:249–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- U54 HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD083091/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 HL085197/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K011154/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M000532/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0801843/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30HD002274/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA160080/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 100140/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 NS064077/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0700073/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 HD002274/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA160080/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT091310/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01NS064077/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

