Conjunctive input processing drives feature selectivity in hippocampal CA1 neurons
- PMID: 26167906
- PMCID: PMC4888374
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4062
Conjunctive input processing drives feature selectivity in hippocampal CA1 neurons
Abstract
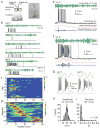
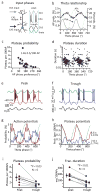
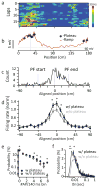
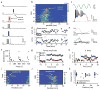
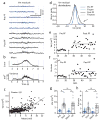
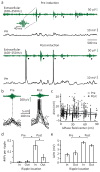
Feature-selective firing allows networks to produce representations of the external and internal environments. Despite its importance, the mechanisms generating neuronal feature selectivity are incompletely understood. In many cortical microcircuits the integration of two functionally distinct inputs occurs nonlinearly through generation of active dendritic signals that drive burst firing and robust plasticity. To examine the role of this processing in feature selectivity, we recorded CA1 pyramidal neuron membrane potential and local field potential in mice running on a linear treadmill. We found that dendritic plateau potentials were produced by an interaction between properly timed input from entorhinal cortex and hippocampal CA3. These conjunctive signals positively modulated the firing of previously established place fields and rapidly induced new place field formation to produce feature selectivity in CA1 that is a function of both entorhinal cortex and CA3 input. Such selectivity could allow mixed network level representations that support context-dependent spatial maps.
Figures


Comment in
-
The binding solution?Nat Neurosci. 2015 Aug;18(8):1060-2. doi: 10.1038/nn.4075. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26216459 No abstract available.
References
-
- Shepherd GM. The Synaptic Organization of the Brain. 5. Oxford University Press; New York: 2004.
-
- Steward O, Scoville SA. Cells of origin of entorhinal cortical afferents to the hippocampus and fascia dentata of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976;169:347–370. - PubMed
-
- Megias M, Emri Z, Freund TF, Gulyas AI. Total number and distribution of inhibitory and excitatory synapses on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Neuroscience. 2001;102:527–540. - PubMed
-
- Cauller LJ, Clancy B, Connors BW. Backward cortical projections to primary somatosensory cortex in rats extend long horizontal axons in layer I. J Comp Neurol. 1998;390:297–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

