Bariatric Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with BMI <30 kg/m2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26167910
- PMCID: PMC4500506
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132335
Bariatric Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with BMI <30 kg/m2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and objective: The role of bariatric surgery in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) remains unclear, and its use in clinical practice is controversial. We conducted a systemic review and meta-analysis to investigate the metabolic changes after surgical treatment in diabetic patients with body mass index (BMI) <30 kg/m2.
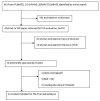
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search in MEDLINE (PubMed), EMBASE and the Cochrane Library of published articles from January 2000 to April 2013 reporting the clinical outcome changes in various metabolic outcomes in diabetic patients with BMI <30 kg/m2.
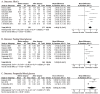
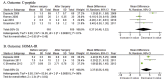
Results: Ten prospective studies including 290 patients were included in the meta-analysis. Bariatric surgery led to an overall 2.79 kg/m2 [95%CI 2.05~3.53, P<0.00001] reduction in BMI, a 1.88%[95%CI 1.32~2.43, P<0.00001] reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin, a 3.70 mmol/L [95%CI, 1.93~5.47, P<0.00001] reduction in fasting blood glucose, a 6.69 mmol/L [95%CI, 2.29~11.08, P=0.003] reduction in postprandial glucose, anda 3.37 [95%CI 0.55~6.18, P=0.02] reduction in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). After surgical treatment, 76.2% of the patients were insulin free, and 61.8% patients were off medication. In total, 90(42.4%), 10(37%) and 34(37.2%) patients had post-surgical HbA1c levels of <6%,<6.5% and<7%, respectively. No deaths were observed in the included studies, and the major complication rate was 6.2%.
Conclusions: Based on the currently available data, bariatric surgery might improve glycemic control and weight loss in a very limited range with a doubled surgical complication rate in drug-refractory T2DM patients with BMI <30 kg/m2. It remains too premature to suggest bariatric surgery for non-obese T2DM patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, Brown BM, et al. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 1995;222(3):339–50; discussion 50–2. Epub 1995/09/01. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc1234815. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

