Mutations in SLC25A46, encoding a UGO1-like protein, cause an optic atrophy spectrum disorder
- PMID: 26168012
- PMCID: PMC4520737
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3354
Mutations in SLC25A46, encoding a UGO1-like protein, cause an optic atrophy spectrum disorder
Abstract
Dominant optic atrophy (DOA) and axonal peripheral neuropathy (Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2, or CMT2) are hereditary neurodegenerative disorders most commonly caused by mutations in the canonical mitochondrial fusion genes OPA1 and MFN2, respectively. In yeast, homologs of OPA1 (Mgm1) and MFN2 (Fzo1) work in concert with Ugo1, for which no human equivalent has been identified thus far. By whole-exome sequencing of patients with optic atrophy and CMT2, we identified four families with recessive mutations in SLC25A46. We demonstrate that SLC25A46, like Ugo1, is a modified carrier protein that has been recruited to the outer mitochondrial membrane and interacts with the inner membrane remodeling protein mitofilin (Fcj1). Loss of function in cultured cells and in zebrafish unexpectedly leads to increased mitochondrial connectivity, while severely affecting the development and maintenance of neurons in the fish. The discovery of SLC25A46 strengthens the genetic overlap between optic atrophy and CMT2 while exemplifying a new class of modified solute transporters linked to mitochondrial dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures

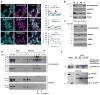
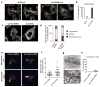



References
-
- Delettre C, Lenaers G, Pelloquin L, Belenguer P, Hamel CP. OPA1 (Kjer type) dominant optic atrophy: a novel mitochondrial disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2002;75:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Alexander C, et al. OPA1, encoding a dynamin-related GTPase, is mutated in autosomal dominant optic atrophy linked to chromosome 3q28. 2000;26 - PubMed
-
- Züchner S, et al. Mutations in the mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin 2 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 2A. Nat Genet. 2004;36:449–51. - PubMed
-
- Chan DC. Dissecting mitochondrial fusion. Dev Cell. 2006;11:592–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS073748/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105781/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM07863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM112179/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS065712/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC012564/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM112179/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Department of Health/United Kingdom
- R01DC012564/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM071775/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM105781/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 NS092238/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54NS065712/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071775/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS092238/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

