Differential Regulation of ERK1/2 and mTORC1 Through T1R1/T1R3 in MIN6 Cells
- PMID: 26168033
- PMCID: PMC4517997
- DOI: 10.1210/ME.2014-1181
Differential Regulation of ERK1/2 and mTORC1 Through T1R1/T1R3 in MIN6 Cells
Abstract
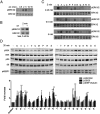
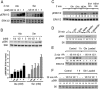
The MAPKs ERK1/2 respond to nutrients and other insulin secretagogues in pancreatic β-cells and mediate nutrient-dependent insulin gene transcription. Nutrients also stimulate the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) to regulate protein synthesis. We showed previously that activation of both ERK1/2 and mTORC1 in the MIN6 pancreatic β-cell-derived line by extracellular amino acids (AAs) is at least in part mediated by the heterodimeric T1R1/T1R3, a G protein-coupled receptor. We show here that AAs differentially activate these two signaling pathways in MIN6 cells. Pretreatment with pertussis toxin did not prevent the activation of either ERK1/2 or mTORC1 by AAs, indicating that G(I) is not central to either pathway. Although glucagon-like peptide 1, an agonist for a G(s-)coupled receptor, activated ERK1/2 well and mTORC1 to a small extent, AAs had no effect on cytosolic cAMP accumulation. Ca(2+) entry is required for ERK1/2 activation by AAs but is dispensable for AA activation of mTORC1. Pretreatment with UBO-QIC, a selective G(q) inhibitor, reduced the activation of ERK1/2 but had little effect on the activation of mTORC1 by AAs, suggesting a differential requirement for G(q). Inhibition of G(12/13) by the overexpression of the regulator of G protein signaling domain of p115 ρ-guanine nucleotide exchange factor had no effect on mTORC1 activation by AAs, suggesting that these G proteins are also not involved. We conclude that AAs regulate ERK1/2 and mTORC1 through distinct signaling pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Methionine Regulates mTORC1 via the T1R1/T1R3-PLCβ-Ca2+-ERK1/2 Signal Transduction Process in C2C12 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 11;17(10):1684. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101684. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27727170 Free PMC article.
-
The ERK1/2 and mTORC1 Signaling Pathways Are Involved in the Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor-Mediated Proliferation of SNU-407 Colon Cancer Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Dec;117(12):2854-2863. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25597. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27167250
-
Muscarinic control of MIN6 pancreatic β cells is enhanced by impaired amino acid signaling.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):14370-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.565069. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24695728 Free PMC article.
-
Key mediators of intracellular amino acids signaling to mTORC1 activation.Amino Acids. 2015 May;47(5):857-67. doi: 10.1007/s00726-015-1937-x. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Amino Acids. 2015. PMID: 25701492 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Understanding Amino Acid Sensing Mechanisms that Regulate mTORC1.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 29;17(10):1636. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101636. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27690010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
On the selectivity of the Gαq inhibitor UBO-QIC: A comparison with the Gαi inhibitor pertussis toxin.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 May 1;107:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26954502 Free PMC article.
-
An experimental strategy to probe Gq contribution to signal transduction in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100472. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100472. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33639168 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine Regulates mTORC1 via the T1R1/T1R3-PLCβ-Ca2+-ERK1/2 Signal Transduction Process in C2C12 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 11;17(10):1684. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101684. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27727170 Free PMC article.
-
Savory Signaling: T1R Umami Receptor Modulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Store Content and Release Dynamics in Airway Epithelial Cells.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 18;15(3):493. doi: 10.3390/nu15030493. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36771200 Free PMC article.
-
Sucralose activates an ERK1/2-ribosomal protein S6 signaling axis.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Jan 18;7(2):174-186. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12172. eCollection 2017 Feb. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28174684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petersen HV, Jensen JN, Stein R, Serup P. Glucose induced MAPK signalling influences NeuroD1-mediated activation and nuclear localization. FEBS Lett. 2002;528:241–245. - PubMed
-
- Khoo S, Griffen SC, Xia Y, Baer R, German MS, Cobb MH. Regulation of insulin gene transcription by extracellular-signal regulated protein kinases (ERK) 1 and 2 in pancreatic β cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:32969–32977. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence MC, McGlynn K, Park BH, Cobb MH. ERK1/2-dependent activation of transcription factors required for acute and chronic effects of glucose on the insulin gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26751–26759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

