Rme-8 depletion perturbs Notch recycling and predisposes to pathogenic signaling
- PMID: 26169355
- PMCID: PMC4508892
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201411001
Rme-8 depletion perturbs Notch recycling and predisposes to pathogenic signaling
Erratum in
-
Rme-8 depletion perturbs Notch recycling and predisposes to pathogenic signaling.J Cell Biol. 2015 Aug 3;210(3):517. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20141100107172015c. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26240186 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
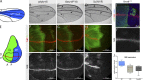
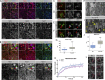
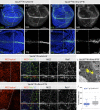
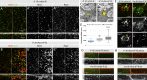
Notch signaling is a major regulator of cell fate, proliferation, and differentiation. Like other signaling pathways, its activity is strongly influenced by intracellular trafficking. Besides contributing to signal activation and down-regulation, differential fluxes between trafficking routes can cause aberrant Notch pathway activation. Investigating the function of the retromer-associated DNAJ protein Rme-8 in vivo, we demonstrate a critical role in regulating Notch receptor recycling. In the absence of Rme-8, Notch accumulated in enlarged tubulated Rab4-positive endosomes, and as a consequence, signaling was compromised. Strikingly, when the retromer component Vps26 was depleted at the same time, Notch no longer accumulated and instead was ectopically activated. Likewise, depletion of ESCRT-0 components Hrs or Stam in combination with Rme-8 also led to high levels of ectopic Notch activity. Together, these results highlight the importance of Rme-8 in coordinating normal endocytic recycling route and reveal that its absence predisposes toward conditions in which pathological Notch signaling can occur.
© 2015 Gomez-Lamarca et al.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

