Realistic wave-optics simulation of X-ray phase-contrast imaging at a human scale
- PMID: 26169570
- PMCID: PMC4500945
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12011
Realistic wave-optics simulation of X-ray phase-contrast imaging at a human scale
Abstract
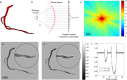
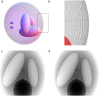
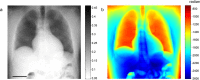
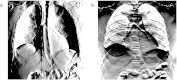
X-ray phase-contrast imaging (XPCI) can dramatically improve soft tissue contrast in X-ray medical imaging. Despite worldwide efforts to develop novel XPCI systems, a numerical framework to rigorously predict the performance of a clinical XPCI system at a human scale is not yet available. We have developed such a tool by combining a numerical anthropomorphic phantom defined with non-uniform rational B-splines (NURBS) and a wave optics-based simulator that can accurately capture the phase-contrast signal from a human-scaled numerical phantom. Using a synchrotron-based, high-performance XPCI system, we provide qualitative comparison between simulated and experimental images. Our tool can be used to simulate the performance of XPCI on various disease entities and compare proposed XPCI systems in an unbiased manner.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wave optics simulation of grating-based X-ray phase-contrast imaging using 4D Mouse Whole Body (MOBY) phantom.Med Phys. 2020 Nov;47(11):5761-5771. doi: 10.1002/mp.14479. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32969031
-
Hybrid framework for feasible modeling of an edge illumination X-ray phase-contrast imaging system at a human scale.Phys Med. 2017 Aug;40:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.05.067. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Phys Med. 2017. PMID: 28729133
-
Fluence adaptation for contrast-based dose optimization in x-ray phase-contrast imaging.Med Phys. 2021 Oct;48(10):6106-6120. doi: 10.1002/mp.15189. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34432891
-
The advent of anthropomorphic three-dimensional breast phantoms for X-ray imaging.Phys Med. 2020 Nov;79:145-161. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.11.025. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Phys Med. 2020. PMID: 33321469 Review.
-
Edge-illumination x-ray phase-contrast imaging.J Phys Condens Matter. 2021 Jul 13;33(36):363002. doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ac0e6e. J Phys Condens Matter. 2021. PMID: 34167096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A generalized quantitative interpretation of dark-field contrast for highly concentrated microsphere suspensions.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 13;6:35259. doi: 10.1038/srep35259. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27734931 Free PMC article.
-
Realistic wave-optics simulation of X-ray dark-field imaging at a human scale.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 23;15(1):26748. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12047-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40702112 Free PMC article.
-
Tomography of dark-field scatter including single-exposure Moiré fringe analysis with X-ray biprism interferometry-A simulation study.Med Phys. 2021 Oct;48(10):6293-6311. doi: 10.1002/mp.15134. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34407202 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-contrast imaging with a compact x-ray light source: system design.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017 Oct;4(4):043503. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.4.043503. Epub 2017 Nov 23. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017. PMID: 29201939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hubbell J. H. & Seltzer S. M. Tables of x-ray mass attenuation coefficients and mass energy-absorption coefficients. National Institute of Standards and Technology (1996).
-
- Paganin D. M. Coherent X-ray optics (Oxford University Press, USA, 2006).
-
- Keyriläinen J. et al. Phase-contrast X-ray imaging of breast. Acta Radiol. 51, 866–884 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Castelli E. et al. Mammography with synchrotron radiation: first clinical experience with phase-detection technique. Radiology 259, 684–694 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Longo R. et al. Clinical study in phase-contrast mammography: image-quality analysis. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 372, 20130025 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

