A genome-wide association study identifies variants in KCNIP4 associated with ACE inhibitor-induced cough
- PMID: 26169577
- PMCID: PMC4713364
- DOI: 10.1038/tpj.2015.51
A genome-wide association study identifies variants in KCNIP4 associated with ACE inhibitor-induced cough
Abstract
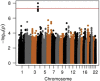
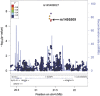
The most common side effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) drugs is cough. We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of ACEi-induced cough among 7080 subjects of diverse ancestries in the Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) network. Cases were subjects diagnosed with ACEi-induced cough. Controls were subjects with at least 6 months of ACEi use and no cough. A GWAS (1595 cases and 5485 controls) identified associations on chromosome 4 in an intron of KCNIP4. The strongest association was at rs145489027 (minor allele frequency=0.33, odds ratio (OR)=1.3 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.2-1.4), P=1.0 × 10(-8)). Replication for six single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in KCNIP4 was tested in a second eMERGE population (n=926) and in the Genetics of Diabetes Audit and Research in Tayside, Scotland (GoDARTS) cohort (n=4309). Replication was observed at rs7675300 (OR=1.32 (1.01-1.70), P=0.04) in eMERGE and at rs16870989 and rs1495509 (OR=1.15 (1.01-1.30), P=0.03 for both) in GoDARTS. The combined association at rs1495509 was significant (OR=1.23 (1.15-1.32), P=1.9 × 10(-9)). These results indicate that SNPs in KCNIP4 may modulate ACEi-induced cough risk.
Figures

References
-
- Zaman MA, Oparil S, Calhoun DA. Drugs targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: 621–636. - PubMed
-
- Overlack A. ACE inhibitor-induced cough and bronchospasm. Incidence, mechanisms and management. Drug Saf 1996; 15: 72–78. - PubMed
-
- Lee YJ, Tsai JC. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene insertion/deletion, not bradykinin B2 receptor -58 T/C gene polymorphism, associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related cough in Chinese female patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metab Clin Exp 2001; 50: 1346–1350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006375/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM010685/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004603/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 085475/B/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK088231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091601/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006382/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004609/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006389/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004599/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 16FTF30130005/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- 084727/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 DK072488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 HG008673/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 085475/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

