Meta-analysis for dorsally displaced distal radius fracture fixation: volar locking plate versus percutaneous Kirschner wires
- PMID: 26169601
- PMCID: PMC4501063
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-015-0252-2
Meta-analysis for dorsally displaced distal radius fracture fixation: volar locking plate versus percutaneous Kirschner wires
Abstract
Background: Dorsally displaced distal radius fractures (DDDRF) are frequent injuries in clinical practice. Traditional percutaneous Kirschner wires (K-wire) and open reduction with volar locking plate (VLP) are the two most common surgical fixation techniques used to manage DDDRF. However, there is no current consensual evidence to guide the selection of one technique over the other. Therefore, we undertook a systematic search and meta-analysis to compare clinical outcomes and complications of these two treatment approaches for DDDRF.
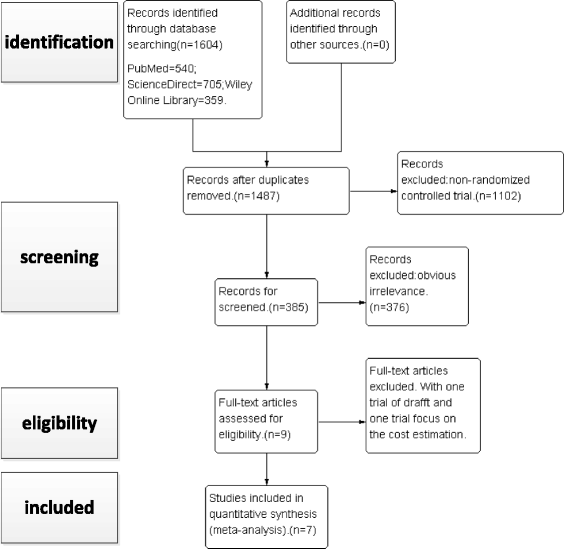
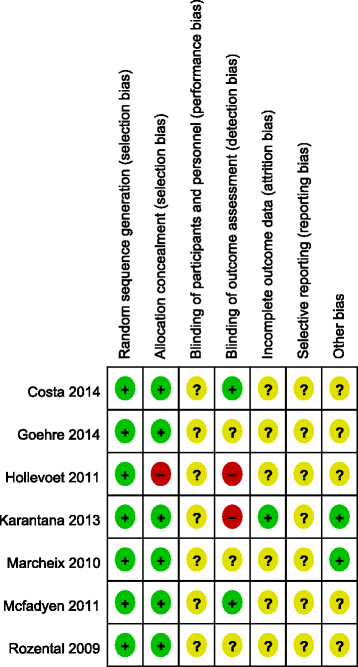
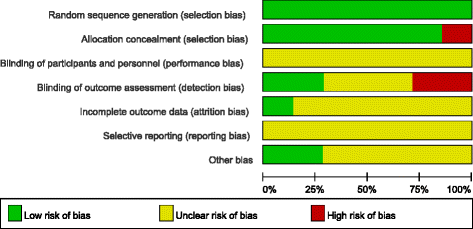
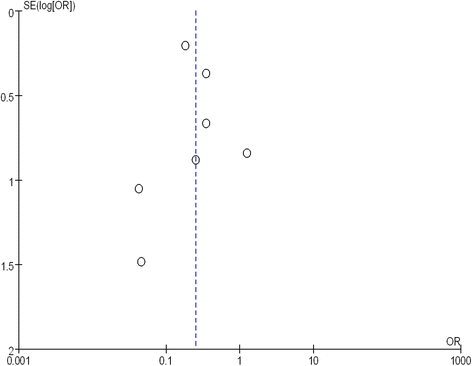
Methods: The following electronic databases were searched by two independent reviewers, up to April 2015: PubMed, ScienceDirect and Wiley Online Library. High-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing VLP and percutaneous K-wire fixation for DDDRF were identified. Pooled mean differences were calculated for the following continuous outcome variables: disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) score, grip strength and wrist range of motion. Pooled odds ratios were calculated for rates of total postoperative complications, including superficial infection, deep infection, complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), neurological injury, tendon rupture, tenosynovitis, loss of reduction and additional surgery to remove hardware. The meta-analysis was completed using RevMan 5.3 software.
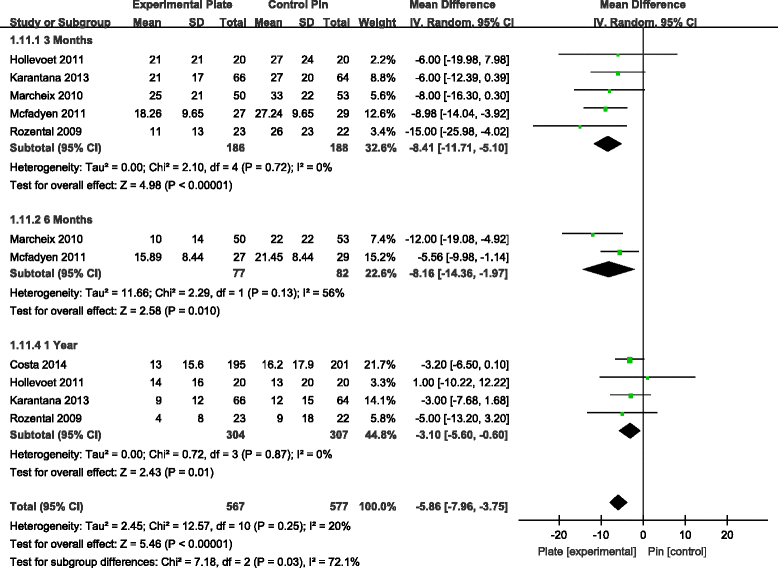
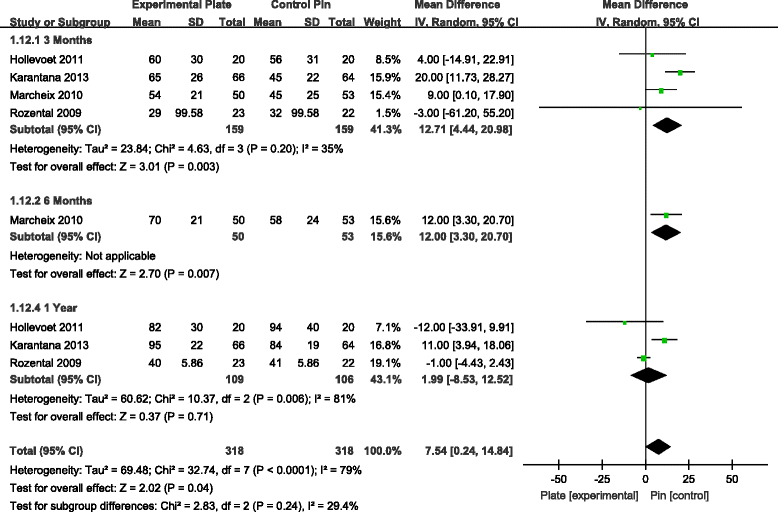
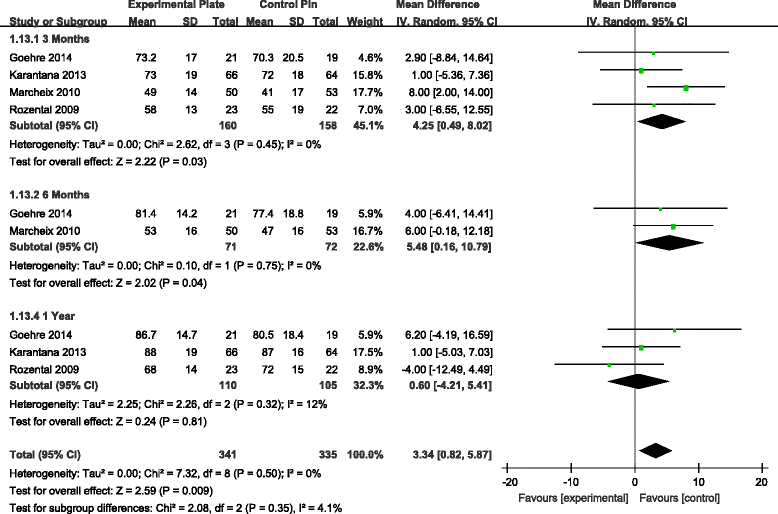
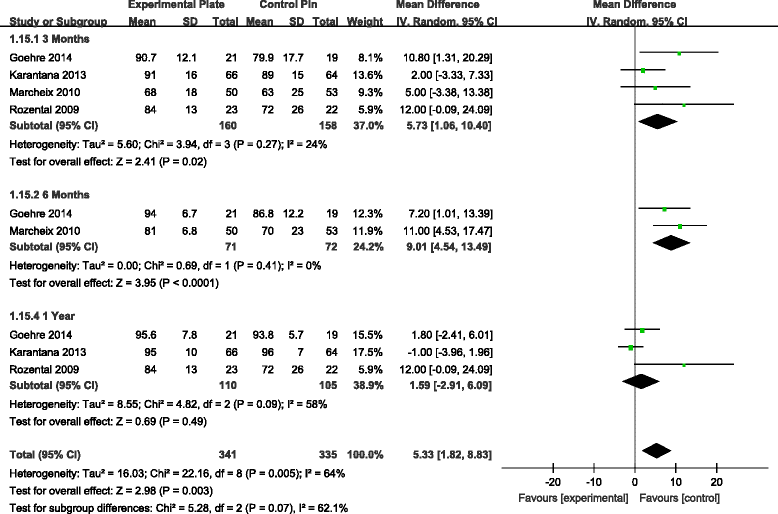
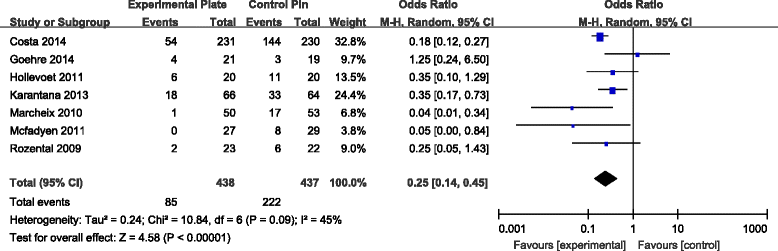
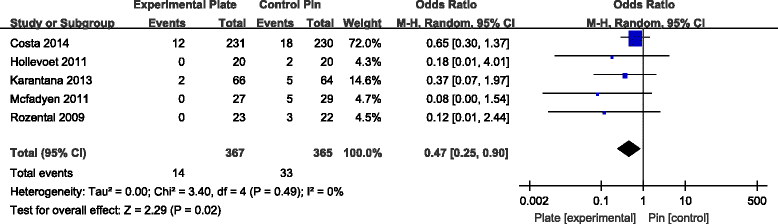
Results: Seven RCTs, with a total of 875 patients, were included in our meta-analysis. Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) with VLP fixation provided statistically lower DASH scores, reduced the incidence of total postoperative complications and specifically lowered the rate of superficial infection, when compared, over a 1-year follow-up, to percutaneous K-wire fixation. VLP fixation also provided significantly better grip strength and range of wrist flexion and supination in the early 6-month postoperative period, compared with percutaneous K-wire fixation.
Conclusion: ORIF with VLP fixation provided lower DASH scores and reduced total postoperative complications, most specifically lowering the risk for postoperative superficial infection compared to K-wire fixation over a 1-year follow-up period. However, superficial pin track infections do not cause clinical debility in the vast majority of cases. Thus, the claim of reduced superficial infection rate may not be clinically important. The only reasonable conclusion that can be drawn is that at present, there is insufficient data even on our meta-analysis to help the clinician make an informed choice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are Volar Locking Plates Superior to Percutaneous K-wires for Distal Radius Fractures? A Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Sep;473(9):3017-27. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4347-1. Epub 2015 May 16. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25981715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complications following internal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking-plate.J Orthop Trauma. 2007 May;21(5):316-22. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e318059b993. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. PMID: 17485996
-
Percutaneous fixation with Kirschner wires versus volar locking-plate fixation in adults with dorsally displaced fracture of distal radius: five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial.Bone Joint J. 2019 Aug;101-B(8):978-983. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.101B8.BJJ-2018-1285.R1. Bone Joint J. 2019. PMID: 31362548 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Volar locking plates versus K-wire/pin fixation for the treatment of distal radial fractures: a systematic review and quantitative synthesis.Br Med Bull. 2015 Sep;115(1):91-110. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldv015. Epub 2015 Apr 26. Br Med Bull. 2015. PMID: 25918348
-
Percutaneous fixation with Kirschner wires versus volar locking plate fixation in adults with dorsally displaced fracture of distal radius: randomised controlled trial.BMJ. 2014 Aug 5;349:g4807. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g4807. BMJ. 2014. PMID: 25096595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comparative Outcomes of Percutaneous K-Wires Versus Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures: A Focus on Stability in Osteoporotic Patients and Both-Bone Distal End Fractures.Cureus. 2024 Nov 4;16(11):e72981. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72981. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39498421 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between Volar Locking Plate and Kirschner Wire Fixation for Unstable Distal Radius Fracture: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Wrist Surg. 2023 Apr 14;13(5):469-480. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1768235. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Wrist Surg. 2023. PMID: 39296653 Free PMC article.
-
Experience of Kapandji technique in treating Colles' fracture in central region of Vietnam.SICOT J. 2022;8:41. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2022040. Epub 2022 Sep 28. SICOT J. 2022. PMID: 36169336 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of the distal radius fractures with percutaneous pinning: evolution to the HK2 system.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018 Dec;28(8):1477-1485. doi: 10.1007/s00590-018-2221-z. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018. PMID: 29869724
-
Long-term outcome for patients with distal radius fractures treated with volar locking plates versus percutaneous wires.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 12;19(11):e0307763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307763. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39531478 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

