Rationale, design and methods for the 22 year follow-up of the Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) Study
- PMID: 26169918
- PMCID: PMC4501054
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1944-6
Rationale, design and methods for the 22 year follow-up of the Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) Study
Abstract
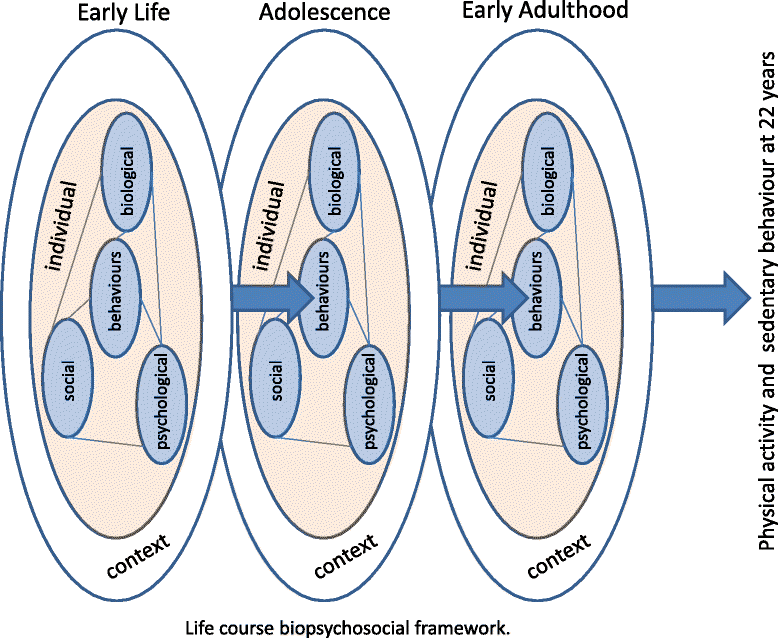
Background: Young adulthood is a critical life period for health and health behaviours. Related measurements collected before and after birth, and during childhood and adolescence can provide a life-course analysis of important factors that contribute to health and behaviour in young adulthood. The Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) Study has collected a large number of such measurements during the fetal, perinatal, infancy, childhood and adolescence periods and plans to relate them to common health issues and behaviours in young adults, including spinal pain, asthma, sleep disorders, physical activity and sedentary behaviour and, work absenteeism and presenteeism. The aim of this paper is to describe the rationale, design and methods of the 22 year follow-up of the Raine Study cohort.
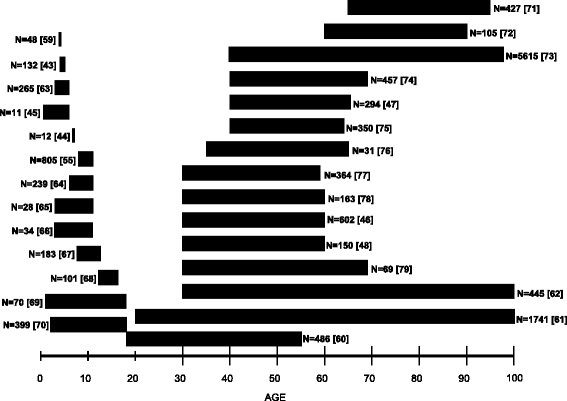
Methods/design: The Raine Study is a prospective cohort study. Participants still active in the cohort (n = 2,086) were contacted around the time of their 22nd birthday and invited to participate in the 22 year follow-up. Each was asked to complete a questionnaire, attend a research facility for physical assessment and an overnight sleep study, wear activity monitors for a week, and to maintain a sleep and activity diary over this week. The questionnaire was broad and included questions related to sociodemographics, medical history, quality of life, psychological factors, lifestyle factors, spinal pain, respiratory, sleep, activity and work factors. Physical assessments included anthropometry, blood pressure, back muscle endurance, tissue sensitivity, lung function, airway reactivity, allergic status, 3D facial photographs, cognitive function, and overnight polysomnography.
Discussion: Describing the prevalence of these health issues and behaviours in young adulthood will enable better recognition of the issues and planning of health care resources. Providing a detailed description of the phenotype of these issues will provide valuable information to help educate health professionals of the needs of young adults. Understanding the life-course risk factors of health issues and behaviours in young adulthood will have important health planning implications, supporting the development of targeted interventions to improve current health status and reduce the onset and development of further ill-health across adulthood.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlates of physical activity and sedentary time in young adults: the Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) Study.BMC Public Health. 2018 Jul 25;18(1):916. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5705-1. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30045696 Free PMC article.
-
Western Australian pregnancy cohort (Raine) Study: Generation 1.BMJ Open. 2019 May 27;9(5):e026276. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026276. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31138581 Free PMC article.
-
Multimorbidity is common among young workers and related to increased work absenteeism and presenteeism: results from the population-based Raine Study cohort.Scand J Work Environ Health. 2020 Mar 1;46(2):218-227. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.3858. Epub 2019 Oct 27. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2020. PMID: 31655849
-
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Myopia in Young Adults: Review of Findings From the Raine Study.Front Public Health. 2022 Apr 27;10:861044. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.861044. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35570945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Distribution of Foveal Avascular Zone Parameters Corrected by Lateral Magnification and Their Associations with Retinal Thickness.Ophthalmol Sci. 2022 Mar 1;2(2):100134. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2022.100134. eCollection 2022 Jun. Ophthalmol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36249684 Free PMC article.
-
Historical development of accelerometry measures and methods for physical activity and sedentary behavior research worldwide: A scoping review of observational studies of adults.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 21;17(11):e0276890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276890. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36409738 Free PMC article.
-
Parental pre-pregnancy BMI is a dominant early-life risk factor influencing BMI of offspring in adulthood.Obes Sci Pract. 2016 Mar;2(1):48-57. doi: 10.1002/osp4.28. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Obes Sci Pract. 2016. PMID: 27812379 Free PMC article.
-
Birth cohort studies using symptom diaries for assessing respiratory diseases-a scoping review.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 10;17(2):e0263559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263559. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35143524 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the Effects of Beverage Substitution during Adolescence on Later Obesity Outcomes in Early Adulthood: Results from the Raine Study.Nutrients. 2019 Dec 3;11(12):2928. doi: 10.3390/nu11122928. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31816850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elder GH, Jr, Johnson MK, Crosnoe R. The emergence and development of life course theory. New York: Springer; 2003.
-
- Bonnie RJ, Stroud C, Breiner H. Investing in the Health and Well-Being of Young Adults. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources