Cucurbitacin D induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by inhibiting STAT3 and NF-κB signaling in doxorubicin-resistant human breast carcinoma (MCF7/ADR) cells
- PMID: 26169986
- PMCID: PMC4589559
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-015-2509-9
Cucurbitacin D induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by inhibiting STAT3 and NF-κB signaling in doxorubicin-resistant human breast carcinoma (MCF7/ADR) cells
Abstract
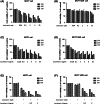
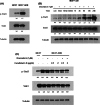
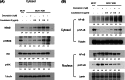
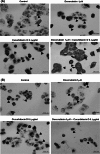
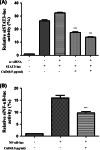
Breast cancer is the most common cancer for women and is a major cause of mortality in women. Doxorubicin is a generally used chemotherapy drug for breast cancer. However, multidrug resistance of breast cancer interferes with the chemotherapy. We examined whether cucurbitacin D affects doxorubicin resistance of MCF7/ADR breast cancer cells. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Levels of p-STAT3, p-NF-κB, IκB, and caspases were measured by Western blot analysis. Nuclear staining of Stat3 and NF-κB was measured by immunocytochemistry. STAT3 and NF-κB transcriptional activity was detected by STAT3 and NF-κB luciferase reporter gene assays. Analysis of cell cycle arrest was performed by flow cytometry. Induction of apoptosis by cucurbitacin D was measured by Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide assay. More than 90% of MCF7/ADR cells lived upon treatment with doxorubicin for 24 h. However, upon treatment with cucurbitacin D, cell death was more than 60%. Co-administration of cucurbitacin D and doxorubicin induced apoptosis, and G2/M cell cycle arrest, and inhibited upregulated Stat3 by doxorubicin on MCF7/ADR cells. Additionally, cucurbitacin D led to an increase in the IκBα level in the cytosol and a decrease in the p-NF-κB level in the nucleus. Finally, cucurbitacin D inhibited translocation of Stat3 and NF-κB and decreased transcriptional activity in the nucleus. Cucurbitacin D decreases cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by inhibiting Stat3 and NF-κB signaling in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells. Cucurbitacin D could be used as a useful compound to treat adriamycin-resistant patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cucurbitacin D; Doxorubicin; MCF7 cell; MCF7/ADR cell; Multidrug resistance.
Figures


References
-
- Sledge GW, Neuberg D, Bernardo P, Ingle JN, Martino S, Rowinsky EK, Wood WC. Phase III trial of doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and the combination of doxorubicin and paclitaxel as front-line chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer: an intergroup trial (E1193) J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:588–592. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.08.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

