Different types of interaction between PCNA and PIP boxes contribute to distinct cellular functions of Y-family DNA polymerases
- PMID: 26170230
- PMCID: PMC4652755
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv712
Different types of interaction between PCNA and PIP boxes contribute to distinct cellular functions of Y-family DNA polymerases
Abstract
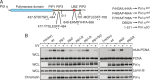
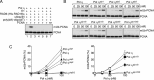
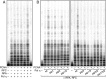
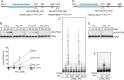
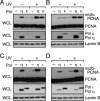
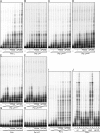
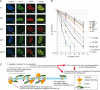
Translesion DNA synthesis (TLS) by the Y-family DNA polymerases Polη, Polι and Polκ, mediated via interaction with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), is a crucial pathway that protects human cells against DNA damage. We report that Polη has three PCNA-interacting protein (PIP) boxes (PIP1, 2, 3) that contribute differentially to two distinct functions, stimulation of DNA synthesis and promotion of PCNA ubiquitination. The latter function is strongly associated with formation of nuclear Polη foci, which co-localize with PCNA. We also show that Polκ has two functionally distinct PIP boxes, like Polη, whereas Polι has a single PIP box involved in stimulation of DNA synthesis. All three polymerases were additionally stimulated by mono-ubiquitinated PCNA in vitro. The three PIP boxes and a ubiquitin-binding zinc-finger of Polη exert redundant and additive effects in vivo via distinct molecular mechanisms. These findings provide an integrated picture of the orchestration of TLS polymerases.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for novel interactions between human translesion synthesis polymerases and proliferating cell nuclear antigen.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10552-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809745200. Epub 2009 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19208623 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin mediates the physical and functional interaction between human DNA polymerases η and ι.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(3):1649-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1277. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23248005 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent coordination of the biological functions of human DNA polymerase iota.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48360-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406511200. Epub 2004 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15342632
-
Regulatory role of ubiquitin in eukaryotic DNA translesion synthesis.Biochemistry. 2013 May 14;52(19):3217-28. doi: 10.1021/bi400194r. Epub 2013 May 1. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23634825 Review.
-
Ubiquitination of PCNA and the polymerase switch in human cells.Cell Cycle. 2004 Aug;3(8):1011-3. Epub 2004 Aug 7. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15280666 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and biochemical characterization of the C-terminal region of the human RTEL1 helicase.Protein Sci. 2024 Sep;33(9):e5093. doi: 10.1002/pro.5093. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 39180489 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of human Pol κ bound to DNA and mono-ubiquitylated PCNA.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 19;12(1):6095. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26251-6. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34667155 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the increased processivity of D-family DNA polymerases in complex with PCNA.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 27;11(1):1591. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15392-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32221299 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive use of error-prone DNA polymerases provides flexibility in genome replication during tumorigenesis.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jul;115(7):2125-2137. doi: 10.1111/cas.16188. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38651239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translesion and Repair DNA Polymerases: Diverse Structure and Mechanism.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:239-261. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012405. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29494238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ohmori H., Friedberg E.C., Fuchs R.P., Goodman M.F., Hanaoka F., Hinkle D., Kunkel T.A., Lawrence C.W., Livneh Z., Nohmi T., et al. The Y-family of DNA polymerases. Mol. Cell. 2001;8:7–8. - PubMed
-
- Masutani C., Kusumoto R., Yamada A., Dohmae N., Yokoi M., Yuasa M., Araki M., Iwai S., Takio K., Hanaoka F. The XPV (xeroderma pigmentosum variant) gene encodes human DNA polymerase η. Nature. 1999;399:700–704. - PubMed
-
- Johnson R.E., Kondratick C.M., Prakash S., Prakash L. hRAD30 mutations in the variant form of xeroderma pigmentosum. Science. 1999;285:263–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

