Effects of Local Pancreatic Renin-Angiotensin System on the Microcirculation of Rat with Severe Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 26170733
- PMCID: PMC4499641
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.4.299
Effects of Local Pancreatic Renin-Angiotensin System on the Microcirculation of Rat with Severe Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is normally related to multiorgan dysfunction and local complications. Studies have found that local pancreatic renin-angiotensin system (RAS) was significantly upregulated in drug-induced SAP. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of angiotensin II receptors inhibitor valsartan on dual role of RAS in SAP in a rat model and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms. 3.8% sodium taurocholate (1 ml/kg) was injected to the pancreatic capsule in order for pancreatitis induction. Rats in the sham group were injected with normal saline in identical locations. We also investigated the regulation of experimentally induced SAP on local RAS expression in the pancreas through determination of the activities of serum amylase, lipase and myeloperoxidase, histological and biochemical analysis, radioimmunoassay, fluorescence quantitative PCR and Western blot analysis. The results indicated that valsartan could effectively suppress the local RAS to protect against experimental acute pancreatitis through inhibition of microcirculation disturbances and inflammation. The results suggest that pancreatic RAS plays a critical role in the regulation of pancreatic functions and demonstrates application potential as AT1 receptor antagonists. Moreover, other RAS inhibitors could be a new therapeutic target in acute pancreatitis.
Keywords: ICAM-1; MDA; P-selectin; Renin-angiotensin System; Severe acute pancreatitis.
Figures
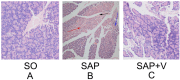

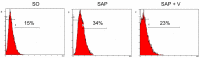
Similar articles
-
The role of the pancreatic renin-angiotensin system in acinar digestive enzyme secretion and in acute pancreatitis.Regul Pept. 2004 Jul 15;119(3):213-9. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.02.003. Regul Pept. 2004. PMID: 15120483
-
Regulated expression of pancreatic renin-angiotensin system in experimental pancreatitis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000 Aug 30;166(2):121-8. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(00)00275-6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10996430
-
Differential effects of saralasin and ramiprilat, the inhibitors of renin-angiotensin system, on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis.Regul Pept. 2003 Mar 28;111(1-3):47-53. doi: 10.1016/s0167-0115(02)00226-4. Regul Pept. 2003. PMID: 12609748
-
Local renin-angiotensin system in the pancreas: the significance of changes by chronic hypoxia and acute pancreatitis.JOP. 2001 Jan;2(1):3-8. JOP. 2001. PMID: 11862015 Review.
-
A local pancreatic renin-angiotensin system: endocrine and exocrine roles.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;35(6):838-46. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00179-6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12676170 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Captopril Compared to Methylprednisolone in L-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jun;63(6):1497-1505. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5036-1. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29594979
-
Angiotensin II receptor blockers and risk of acute pancreatitis - a population based case-control study in Sweden.BMC Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar 7;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12876-017-0595-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28270103 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Device and Computer Algorithm-Based Monitoring of Pancreatic Microcirculation Profiles In Vivo.Pancreas. 2020 Sep;49(8):1075-1082. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001627. Pancreas. 2020. PMID: 32769856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akay C, Yaman H, Oztosun M, Cakir E, Yildirim AO, Eyi YE, Agilli M, Akgul EO, Aydin I, Kaldirim U, Tuncer SK, Eken A, Oztas E, Poyrazoglu Y, Yasar M, Ozkan Y. The protective effects of taurine on experimental acute pancreatitis in a rat model. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2013;32:522–529. - PubMed
-
- Galuppo M, Nocentini G, Mazzon E, Ronchetti S, Esposito E, Riccardi L, Sportoletti P, Di Paola R, Bruscoli S, Riccardi C, Cuzzocrea S. The glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor family-related protein (GITR) is critical to the development of acute pancreatitis in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162:1186–1201. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hartman H, Abdulla A, Awla D, Lindkvist B, Jeppsson B, Thorlacius H, Regnér S. P-selectin mediates neutrophil rolling and recruitment in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2012;99:246–255. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Shi L, Chen M, Chen S, Zou X. Effects of c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway on severe acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Pancreas. 2012;41:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Yubero S, Manso MA, Ramudo L, Vicente S, De Dios I. Dexamethasone down-regulates the inflammatory mediators but fails to reduce the tissue injury in the lung of acute pancreatitis rat models. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2012;25:319–324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

