Oleanolic acid: a promising neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 26170805
- PMCID: PMC4424737
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.155414
Oleanolic acid: a promising neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemia
Figures
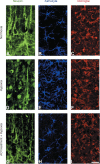
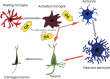
References
-
- Caltana L, Rutolo D, Nieto ML, Brusco A. Further evidence for the neuroprotective role of oleanolic acid in a model of focal brain hypoxia in rats. Neurochem Int. 2014;79:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Camer D, Yu Y, Szabo A, Huang XF. The molecular mechanisms underpinning the therapeutic properties of oleanolic acid, its isomer and derivatives for type 2 diabetes and associated complications. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014;58:1750–1759. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- López-Miranda J, Pérez-Jiménez F, Ros E, De Caterina R, Badimón L, Covas MI, Escrich E, Ordovαs JM, Soriguer F, Abiα R, de la Lastra CA, Battino M, Corella D, Chamorro-Quirós J, Delgado-Lista J, Giugliano D, Esposito K, Estruch R, Fernandez-Real JM, Gaforio JJ, et al. Olive oil and health: summary of the II international conference on olive oil and health consensus report, Jaén and Córdoba (Spain) 2008. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;20:284–294. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
