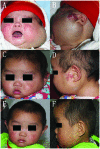
Treatment with propranolol for infantile hemangiomas: A case series of 106 infants
- PMID: 26170911
- PMCID: PMC4487025
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2015.2485
Treatment with propranolol for infantile hemangiomas: A case series of 106 infants
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to investigate the clinical benefit and side effects of propranolol treatment in 106 children with infantile hemangiomas (IHs). A retrospective chart review was conducted on all children who attended the clinic between September 16, 2009 and November 11, 2013. Propranolol was administered in a progressive schedule reaching 1.0-1.5 mg/kg/day, divided into three doses. Demographic data, clinical features, imaging, treatment regimens and outcomes were investigated. Any adverse effects following medication were evaluated and managed accordingly. Preliminary analysis of the data showed the inclusion of 106 children (71 female and 35 male) with a mean age and weight at onset of treatment of 5.1 months and 7.3 kg, respectively. All 106 patients responded positively to treatment. Side effects that required intervention and/or close monitoring included diarrhea (n=10), hypotension (n=7), nightmares (n=2), agitation (n=1) and cold extremities (n=1). No long-term adverse effects were observed in any of the patients. In conclusion, propranolol administered orally at 1.0-1.5 mg/kg/day had a rapid therapeutic effect for resolving IHs with few complications.
Keywords: hemangiomas; infants; propranolol; side effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Propranolol for the Treatment of Infantile Hemangiomas in the Post-Proliferative Phase: A-Single Center Retrospective Study of 31 Cases.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016 Aug;74(8):1623-9. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27055227
-
Clinical Outcomes of Infants With Periorbital Hemangiomas Treated With Oral Propranolol.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016 Nov;74(11):2193-2199. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.04.021. Epub 2016 May 2. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27235180
-
[Treatment of infantile hemangiomas with low-dose propranolol: evaluation of short-term efficacy and safety].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Dec 1;89(44):3130-4. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20193276 Chinese.
-
Propranolol treatment in life-threatening airway hemangiomas: a case series and review of literature.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Nov;77(11):1791-800. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 24074695 Review.
-
Topical propranolol cream in treatment of superficial infantile hemangiomas: a literature review and 4 years of clinical experience.Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2014;23(4):75-8. doi: 10.15570/actaapa.2014.18. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2014. PMID: 25527040 Review.
References
-
- Amer TA, Elwakil TF, Elbasiouny MS. Open rhinoplasty for treatment of nasal tip haemangioma. Eur J Plast Surg. 2007;30:67–73. doi: 10.1007/s00238-007-0152-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources