Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on heart rate variability in hysteroscopy
- PMID: 26170932
- PMCID: PMC4487072
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2015.2497
Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on heart rate variability in hysteroscopy
Abstract
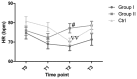
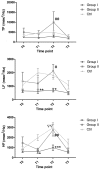
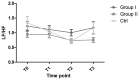
In order to evaluate the effect of different doses of penehyclidine hydrochloride (penehyclidine) on heart rate (HR) and HR variability (HRV) in hysteroscopy, 180 patients (American Society of Anesthesiologists grade I-II) were randomized equally to three groups: 0.5 mg penehyclidine and intravenous anesthesia (group I), 1.0 mg penehyclidine and intravenous anesthesia (group II) and saddle anesthesia combined with intravenous anesthesia (control group). HR and HRV, including total power (TP), low-frequency power (LF), high-frequency power (HF) and the LF to HF ratio (LF/HF), were recorded prior and subsequent to the induction of anesthesia (T0 and T1, respectively), following the start of surgery (T2) and following completion of surgery (T3). HR was lower at T2 than at T0 in the control patients, but no differences were observed in groups I and II. The HR at T2 was increased in group II compared with that in group I. TP in group II was significantly higher compared with that in group I at T2. At T1 and at T2, the LF and HF values were lower in group I than those in the controls. Patients in group II also had higher LF and HF at T2 than patients in group I. The HF was higher at T2 than that at T0 in the controls; however, the HF and LF did not change significantly within groups I and II. No significant differences were observed in the LF/HF ratio among the three groups. At a dose of 0.5 mg, penehyclidine stabilized HRV and did not alter the autonomic nervous modulation of HR. A penehyclidine dose of 1.0 mg may be superior to a dose of 0.5 mg in maintaining HR, but is less effective at balancing sympathetic and parasympathetic activity.
Keywords: heart rate; heart rate variability; hysteroscopy; penehyclidine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of heart rate variability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during spinal anesthesia using dexmedetomidine.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):5395-5403. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150136 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block on autonomic nervous function during CO2-pneumoperitoneum: A randomized double-blind control trial.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Aug;32:255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27290985 Clinical Trial.
-
Heart rate and blood pressure power spectral analysis during calcium channel blocker induced hypotension.Can J Anaesth. 1999 Dec;46(12):1110-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03015517. Can J Anaesth. 1999. PMID: 10608202 Clinical Trial.
-
Heart rate and heart rate variability comparison between postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome versus healthy participants; a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019 Dec 30;19(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-01298-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2019. PMID: 31888497 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate variability and autonomic activity at rest and during exercise in various physiological conditions.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003 Oct;90(3-4):317-25. doi: 10.1007/s00421-003-0953-9. Epub 2003 Sep 12. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003. PMID: 13680241 Review.
Cited by
-
Penehyclidine hydrochloride post-conditioning reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4272-4278. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5089. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29104640 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects and pharmacological properties of penehyclidine hydrochloride.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Oct 5;12:3289-3299. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S177435. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30323561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rossman AC. The physiology of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and its importance in the administration of anesthesia. AANA J. 2011;79:433–440. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
